Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic skin disease with the main symptoms of itching, erythema and squamous lesions, cardiovascular, mental disorders (depression, anxiety, sleep disorders, etc.) and other diseases. In order to better study atopic dermatitis, researchers have developed a variety of animal models of atopic dermatitis on mice, including (1) AD models caused by enhanced skin sensitization using epithelial sensitive antigens, haptens, etc.; (2) genetically engineered mouse AD models; (3) spontaneous AD mouse models.
Biocytogen uses C57BL/6 wild mice and B-hIL4/hIL4R double gene humanized mice on C57BL/6 background to produce dermatitis lesions using oxazolone (OXA) sensitization and continuous challenge to establish AD disease models for efficacy evaluation of AD-related drugs1, 2.
Experimental Animals:C57BL/6,7 weeks old, female
Modeling reagent:OXA
Modeling method:Sensitization—0 days, right ear application
Challenge—7-25 days, right ear application
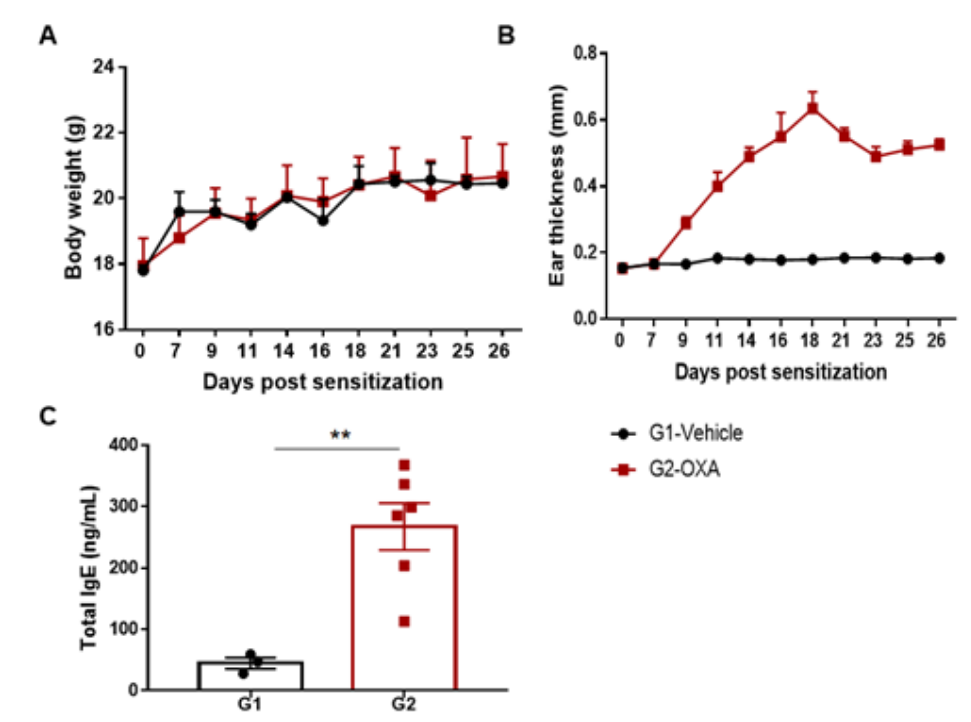
The AD model was induced by OXA in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. (A) Mouse body Weight. (B) Ear thickness. (C) Serum total IgE concentration. Ear thickness and the serum IgE were significantly increased in the OXA -treated group.
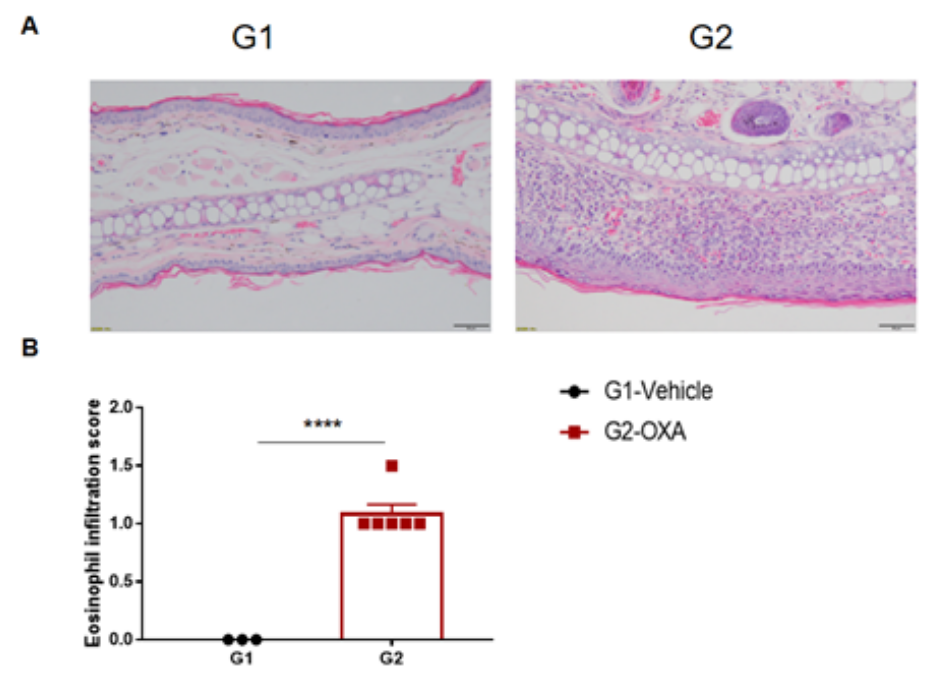
Analysis of ear skin pathology and lymphocyte infiltration in a wild-type C57BL/6 AD model. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of mouse ear tissue sections; (B) Eosinophil infiltration scores in the ear epidermis. The OXA-treated group showed different degrees of stromal cell proliferation, thickening, hyperkeratosis with hypokeratosis, crust, mixed inflammatory cell infiltration in dermis and subcutaneous tissue and other atopic dermatitis-related pathological changes in the epidermis. The infiltration score of eosinophils was significantly higher. The above results demonstrated that OXA could successfully induce AD-like pathology in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.
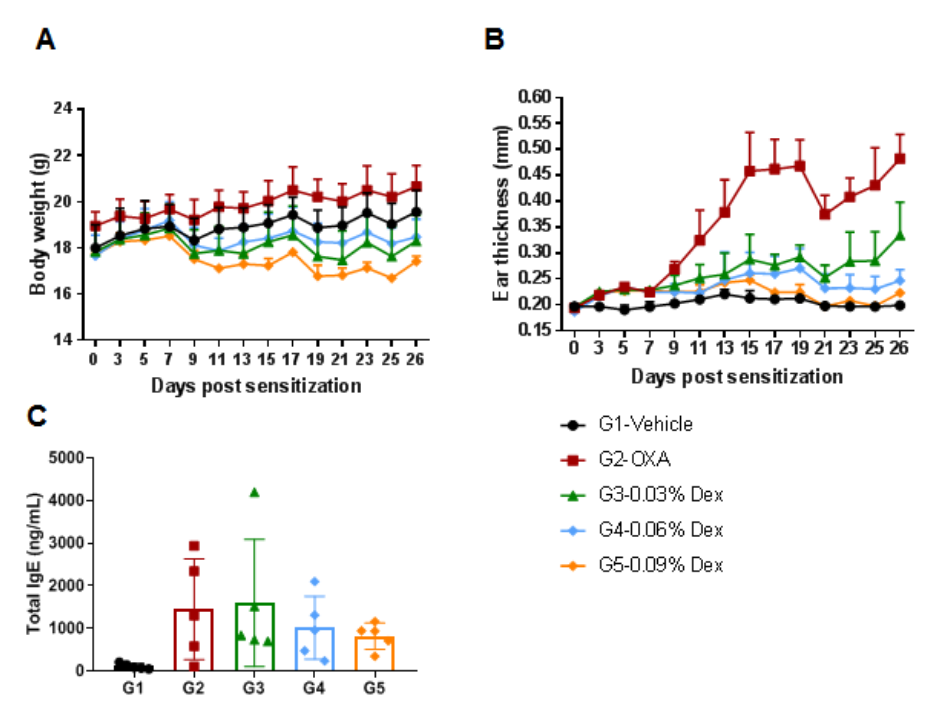
The efficacy of dexamethasone (Dex) was verified in a wild-type C57BL/6 AD model. (A) Mouse body weight. (B) Ear thickness. The results showed that different concentrations of dexamethasone could significantly reduce ear thickness compared with the OXA-only group. The high-dose group (0.09% Dex) completely relieved ear skin edema to the same level as controls. However, it was also associated with significant weight loss compared with the control group. (C) Serum total IgE concentration. The results showed that dexamethasone in G4 medium dose group (0.06% Dex) and G5 high dose group (0.09% Dex) could reduce the concentration of serum total IgE.
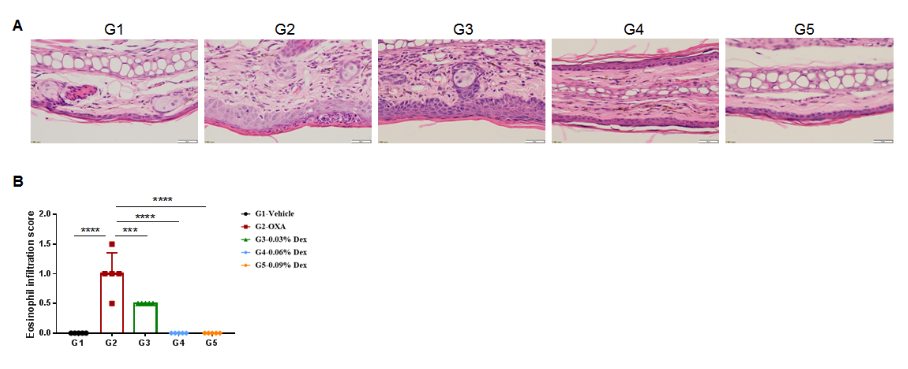
The efficacy of dexamethasone was verified using wild-type AD model. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of mouse ear tissue sections. (B) Eosinophil infiltration score of the ear epidermis. The results showed that pathological changes related to atopic dermatitis, such as stromal cell proliferation, thickening, and mixed inflammatory cell infiltration, were observed in the skin epidermis of the ears of animals in the OXA-treated group (G2), and these phenotypes were significantly alleviated in the Dex-treated groups (G3-G5) compared with the G2 modeling group, especially in the high dose group (0.09% Dex), which returned to baseline. The eosinophil infiltration score in the skin was significantly lower in the G3-G5 group than in the G2 group. Overall, dexamethasone improved atopic dermatitis-related symptoms, with Dex at concentrations of 0.06% and 0.09% having improved efficacy. The above results showed that the AD mouse model could be successfully induced for efficacy evaluation using OXA.
Efficacy Validation on AD model (B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice) for dupilumab (in house)
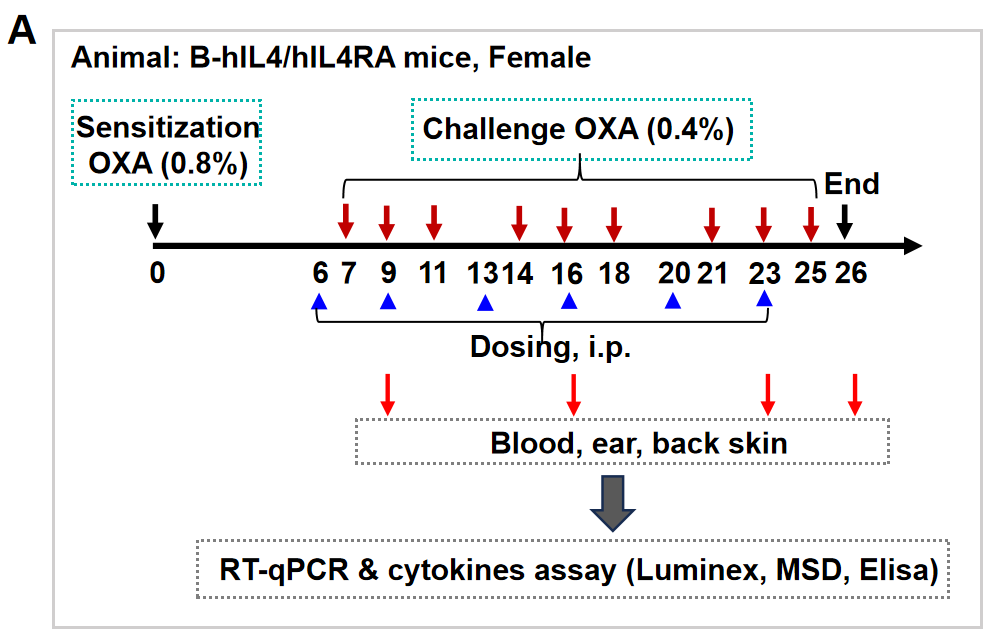
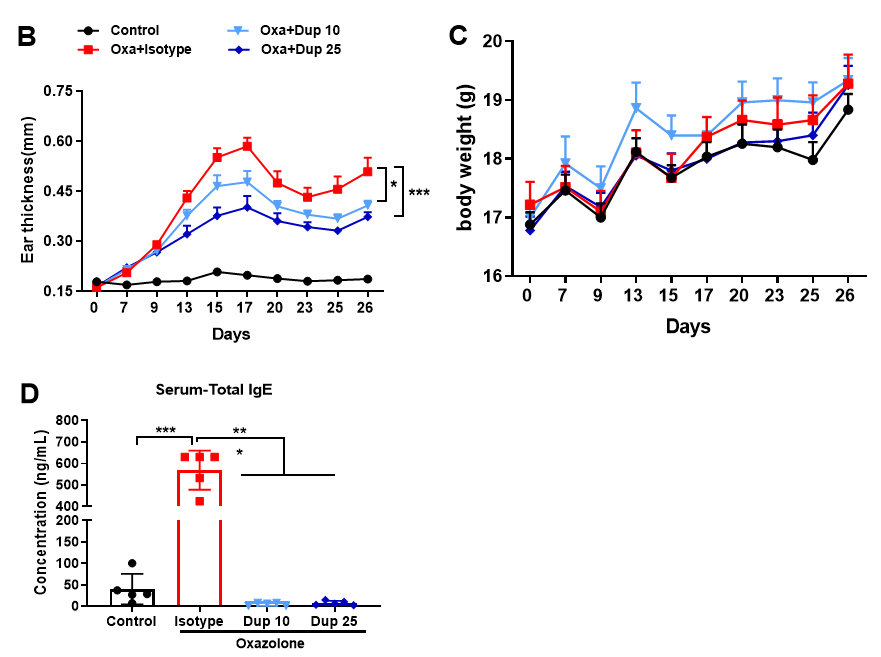
Fig 1. Dupilumab alleviated OXA induced atopic dermatitis in B-hIL4/IL4RA mice. Mice received 0.8% OXA on ear and skin on day 0, then received 0.4% OXA application three times a week from day 7 to day 25. Body weight and ear thickness were recorded after OXA application. Mice received PBS or dupilumab (10, 25 mg/kg) twice a week from day 6 for totally 6 times. Ear, back skin and blood were collected at the end (A). Dupilumab produced no effects on body weight (C). Ear thickness (B) and serum IgE (D) were decreased in dupilumab treated mice.
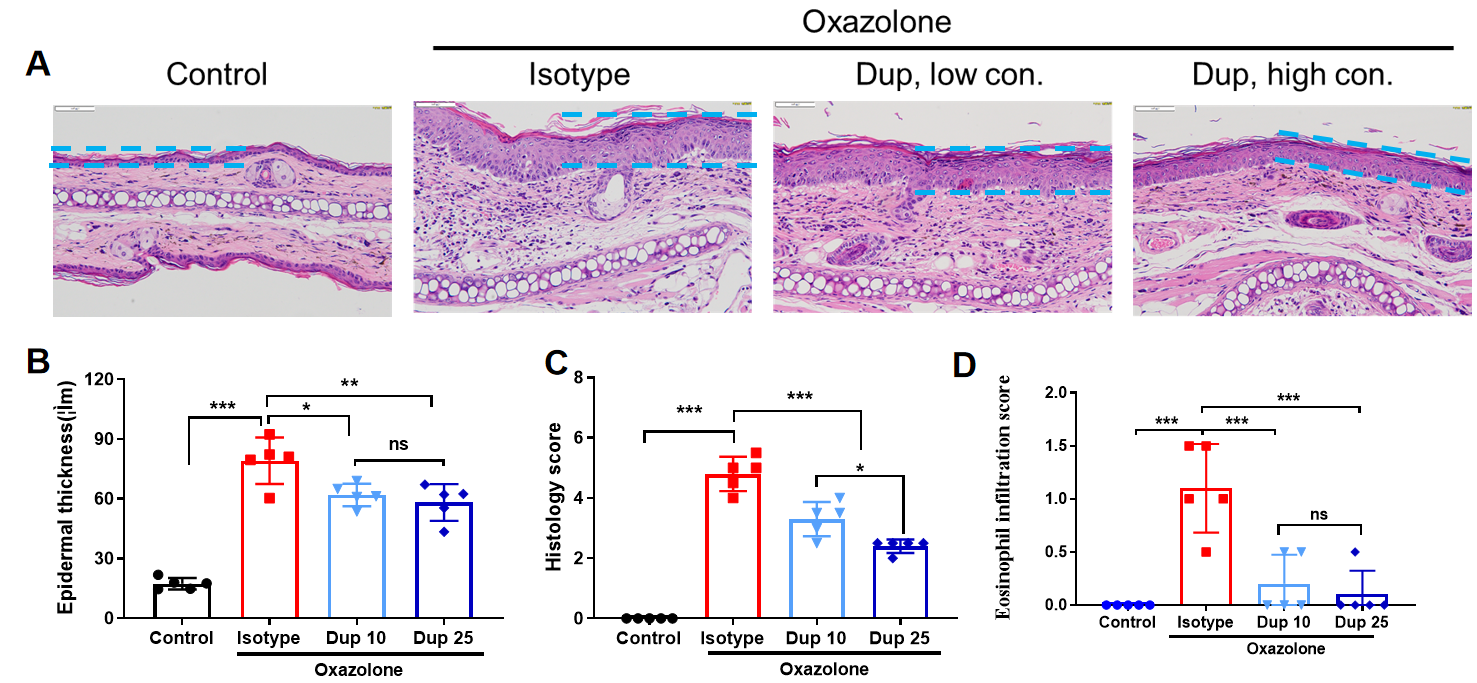
Fig 2. Efficacy of anti-human IL4R antibody in B-hIL4/hIL4R mice. Dose dependent effects of anti-human IL-4R antibody (in house) in oxazolone induced skin lesions in B-hIL4R mice.
Dupilumab reduced OXA induced human IL-4 increase in B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice (Elisa)
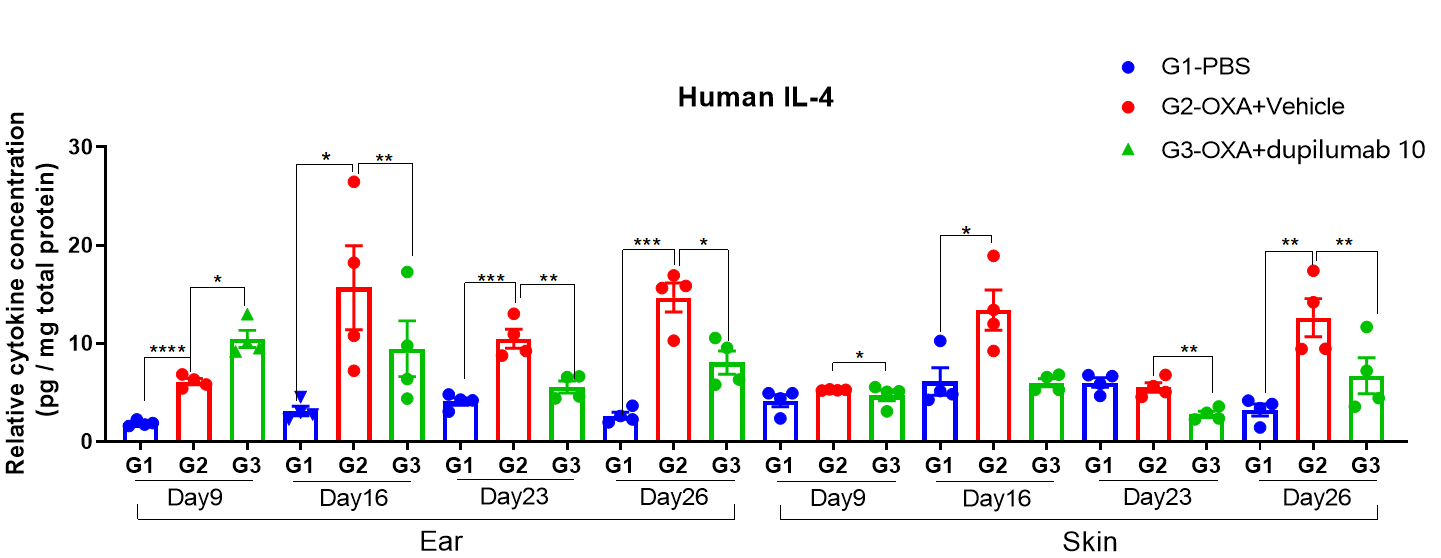
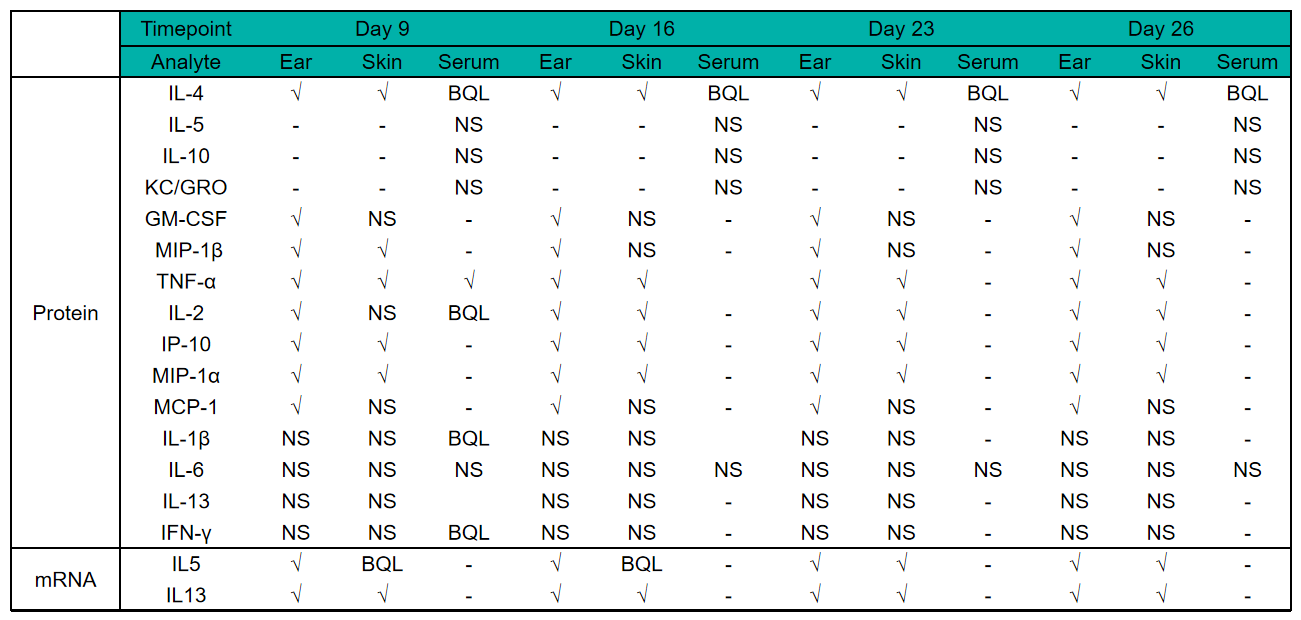
Fig 3. Protain expression analysis in OXA-induced AD model of B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by ELISA. Ear and skin samples of modeling area were collected from at day 9, 16, 26 and 26 and analyzed ELISA. Tissue sample homogenate supernatants were loaded for ELISA detection, and the results were standardized by total protein concentration of the corresponding sample.
Protein expression analysis in OXA-induced AD model of B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by Luminex
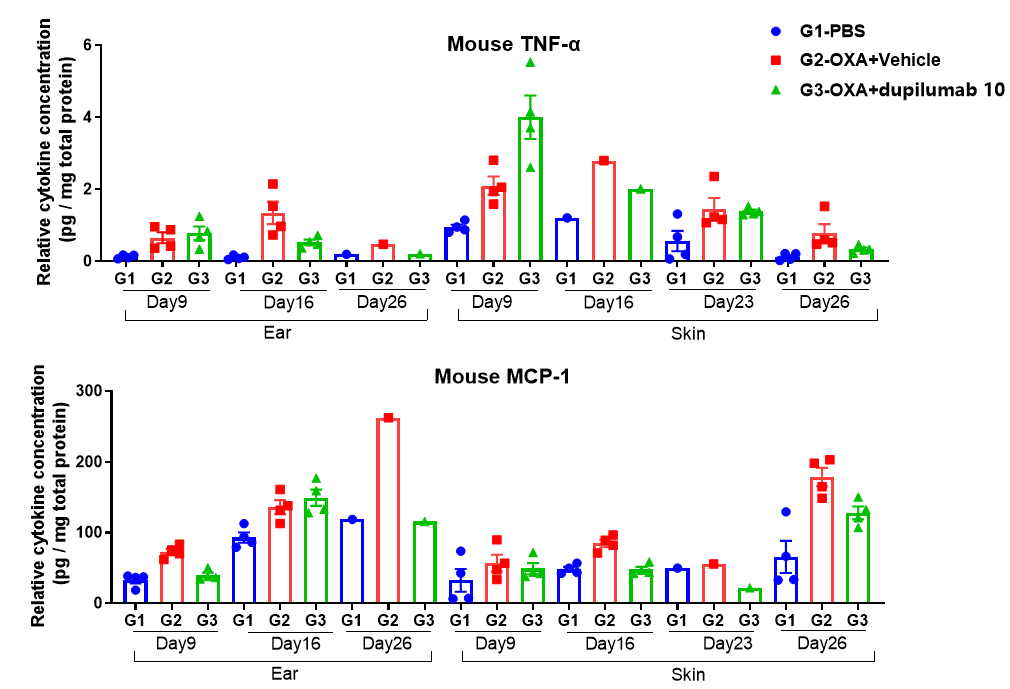
Fig 4. Protain expression analysis in OXA-induced AD model of B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by Luminex. Ear and skin samples of modeling area were collected from at day 9, 16, 26 and 26 and analyzed by Luminex. Tissue sample homogenate supernatants were loaded for detection.
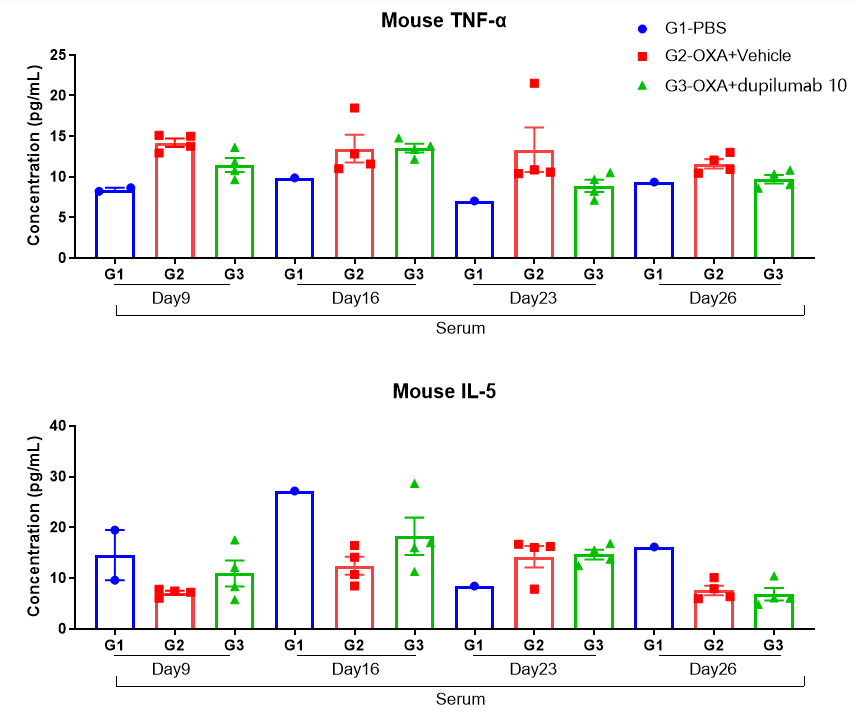
Fig 5. Protain expression analysis in OXA-induced AD model of B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by MSD. Ear and skin samples of modeling area were collected from at day 9, 16, 26 and 26 and analyzed by Luminex. Tissue sample homogenate supernatants were loaded for detection.
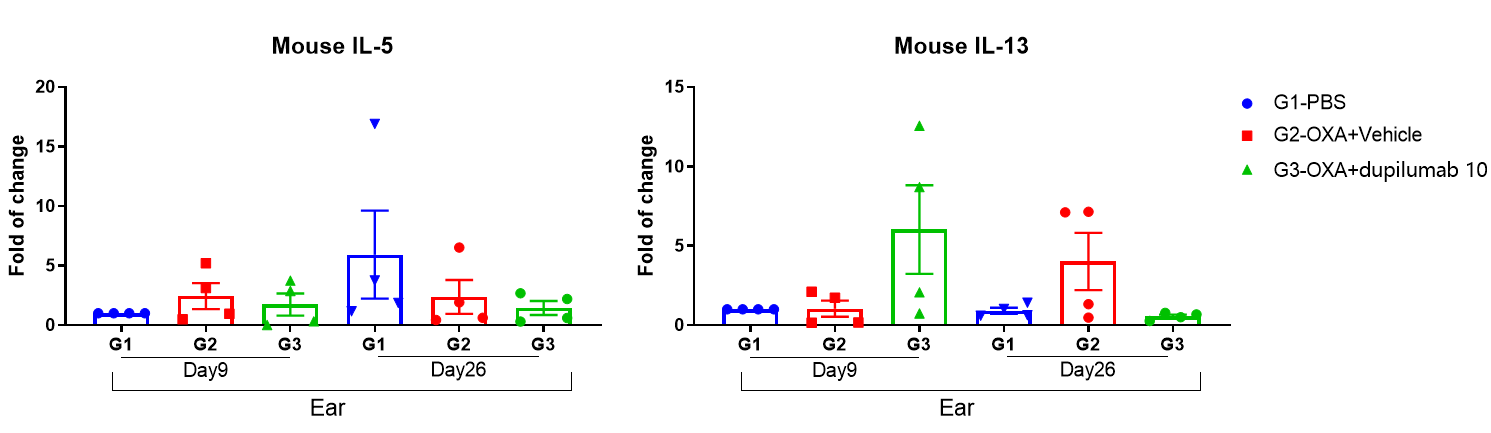
Fig 6. Mouse IL-5 and IL-13 expression analysis in OXA-induced AD model of B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice by qRT-PCR. Ear were collected at day 9 and 26 and total RNA of these samples were extracted. Then RNA samples were reverse transcribed and mouse IL-5, mouse IL-13 levels were measured by qRT-PCR, while mouse GAPDH was used as house keeping gene.


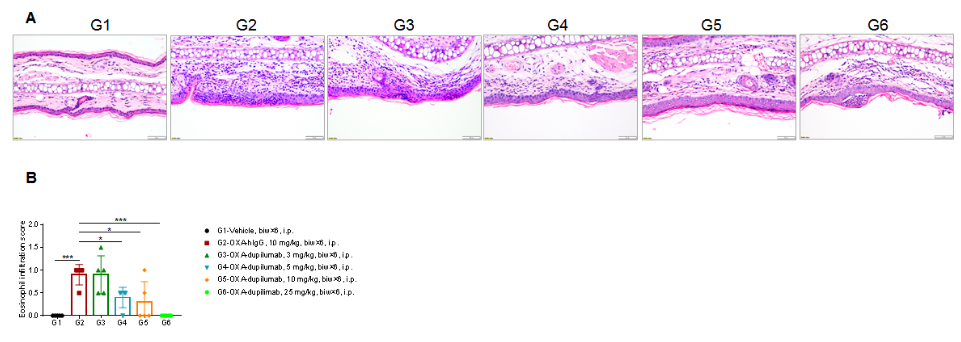
Efficacy of anti-human IL4RA antibody dupilumab (in-house) on skin and lymphocyte infiltration in the ear of B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice with experimental AD.(A)Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of mouse ear tissue sections. (B) Eosinophilic infiltration score of ear skin. The results showed that pathological changes related to atopic dermatitis, such as stromal cell proliferation, thickening, and mixed inflammatory cell infiltration, were observed in the ear skin epidermis of animals in the G2 (OXA + IgG) group, and the pathological changes of the skin diseases were significantly alleviated in the G3-G6 (dupilumab) groups compared with the G2 modeling group. The eosinophil infiltration score in the skin was significantly decreased in the G3-G5 group compared with the G2 group, in a dose-dependent manner. The above results indicate that B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo efficacy evaluation of anti-human IL4RA antibodies.
|
Product name |
Product number |
|
B-hIL4/hIL4RA mice |
120551 |
1. Vatrella, A., Fabozzi, I., Calabrese, C., Maselli, R. & Pelaia, G. Dupilumab: a novel treatment for asthma. J Asthma Allergy 7, 123-130 (2014).
2. Gandhi, N.A. et al. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15, 35-50 (2016).






 +86-10-56967680
+86-10-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn