Acute lung inflammation usually occurs with asthma. Alternaria and papain are allergens disrupting the airway epithelium triggering a rapid inflammation with eosinophils mediated by innate lymphoid cell activation. Intranasal administration of alternaria or papain to mice are able to induces a rapid influx of neutrophils into the lungs, so as to produce lung inflammation [1-2].
Biocytogen has developed a convenient and stable model of ALT and papain-induced acute lung inflammation in C57BL/6 mice.
Establishment of papain induced Pneumonia Mouse Model
Papain-induced Pneumonia
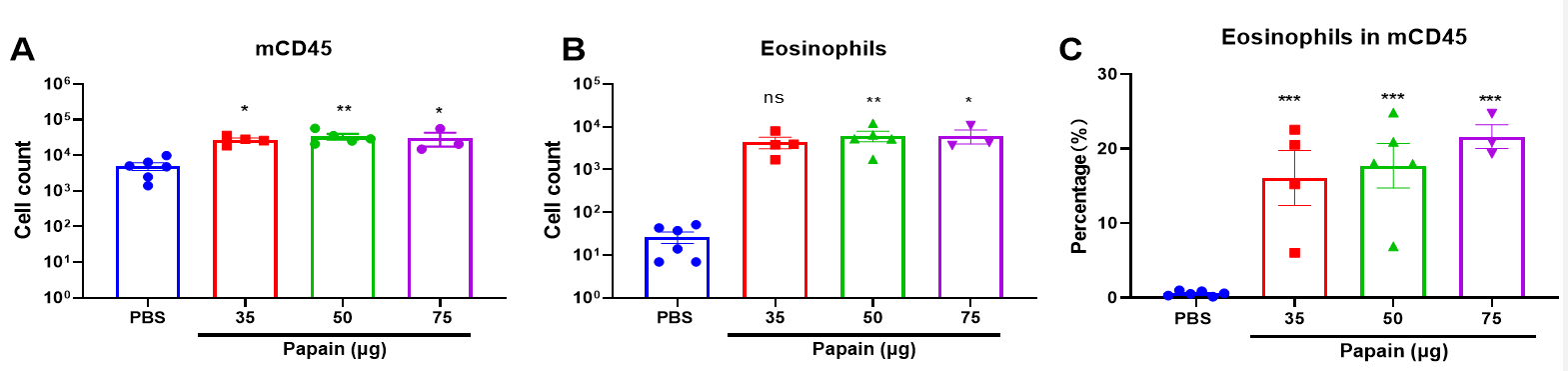
Effects of papain on immune cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Papain-induced mouse model of pneumonia. Mice received different doses of papain (35-75 μg) for 3 days. Bronchoalveolar lavage were collected at the end of the experiment. mCD45 positive cells (A), eosinophils (B) in BALF samples were counted. The percentage of eosinophils in mCD45 was calculated (C). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test, n=5, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
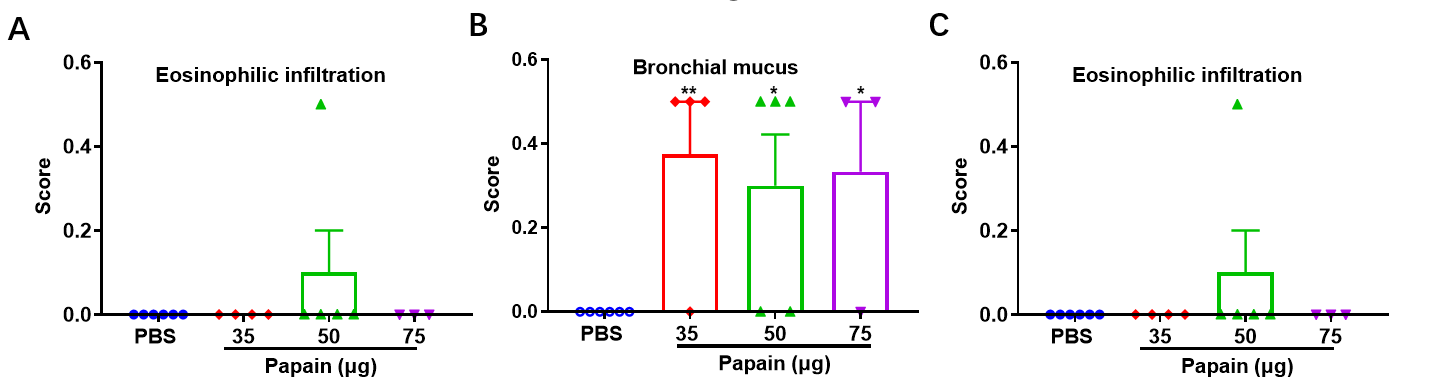
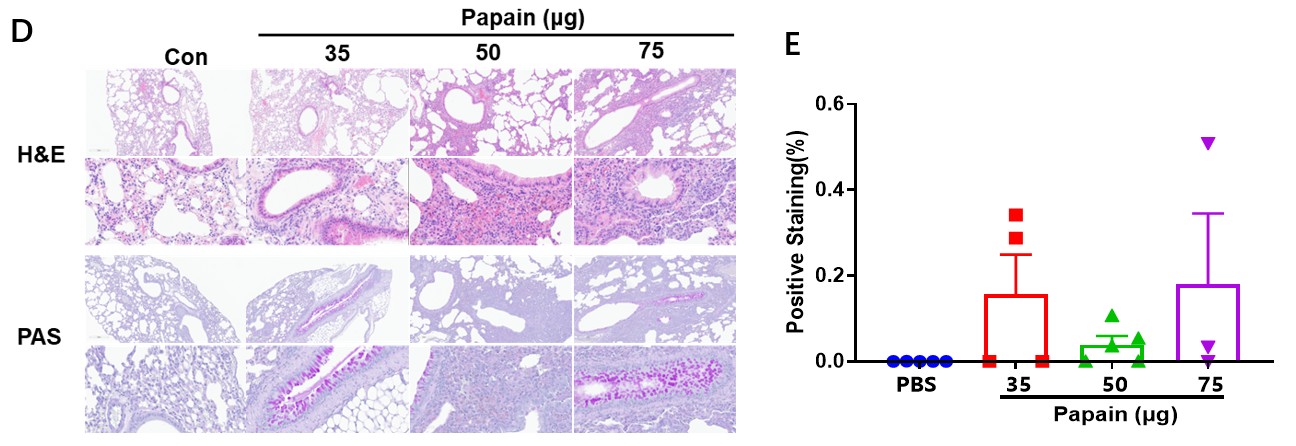
Papain-induced mouse model of pneumonia. Mice received different doses of papain (35-75 μg, i.n.) for 3 consecutive days. (D) Pathological changes were demonstrated by vascular and peribronchial mixed inflammatory cell infiltration and mucus formation in some bronchi. (A-C,E) The score of cells and infiltration of vascular and peribronchial eosinophil were increased after papain treatment.

References
[1] Zhou WS, Zhang J, Toki S, et al. COX Inhibition Increases Alternaria-Induced Pulmonary Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses and IL-33 Release in Mice[J]. J Immunol. 2020, 205(4):1157-1166.
[2] Kabata H , Flamar A L, Mahlakõiv T, et al. Targeted deletion of the TSLP receptor reveals cellular mechanisms that promote type 2 airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13(4) :626-636.
Establishment of ALT-induced Pneumonia Mouse Model
Pneumonia was induced in C57BL/6 mice by nasal administration of ALT (100μg/80μL) or PBS (Control) 4 consecutive times.
Immune Cell Infiltration in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) of Asthmatic Mice
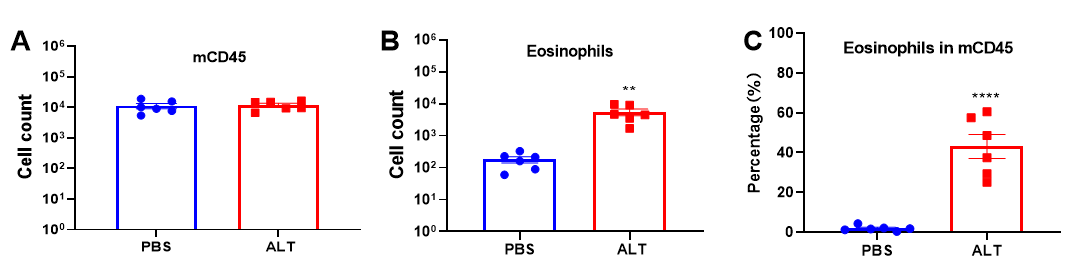
Effects of ALT on immune cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Mice received ALT (100 μg) for 4 consecutive days. Bronchoalveolar lavage were collected at the end of the experiment. mCD45 positive cells (A), eosinophils (B) in BALF samples were counted. The percentage of eosinophils in mCD45 was calculated (C). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test, n=5, **P<0.01 ***P<0.001.
Sepsis, one of the most fatal diseases worldwide, often leads to multiple organ failure, mainly due to uncontrolled inflammatory response [3]. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component of Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin that induces acute inflammation by stimulating host cells to produce proinflammatory cytokines, which is recognized as the main cause of acute organ injury [4].
A convenient and stable model of LPS-induced acute inflammation was developed in C57BL/6 mice.
Establishment of LPS-induced Acute inflammation
Efficacy Validation on Acute inflammation Mouse Models for anti-TLR4 antibody (in-house)
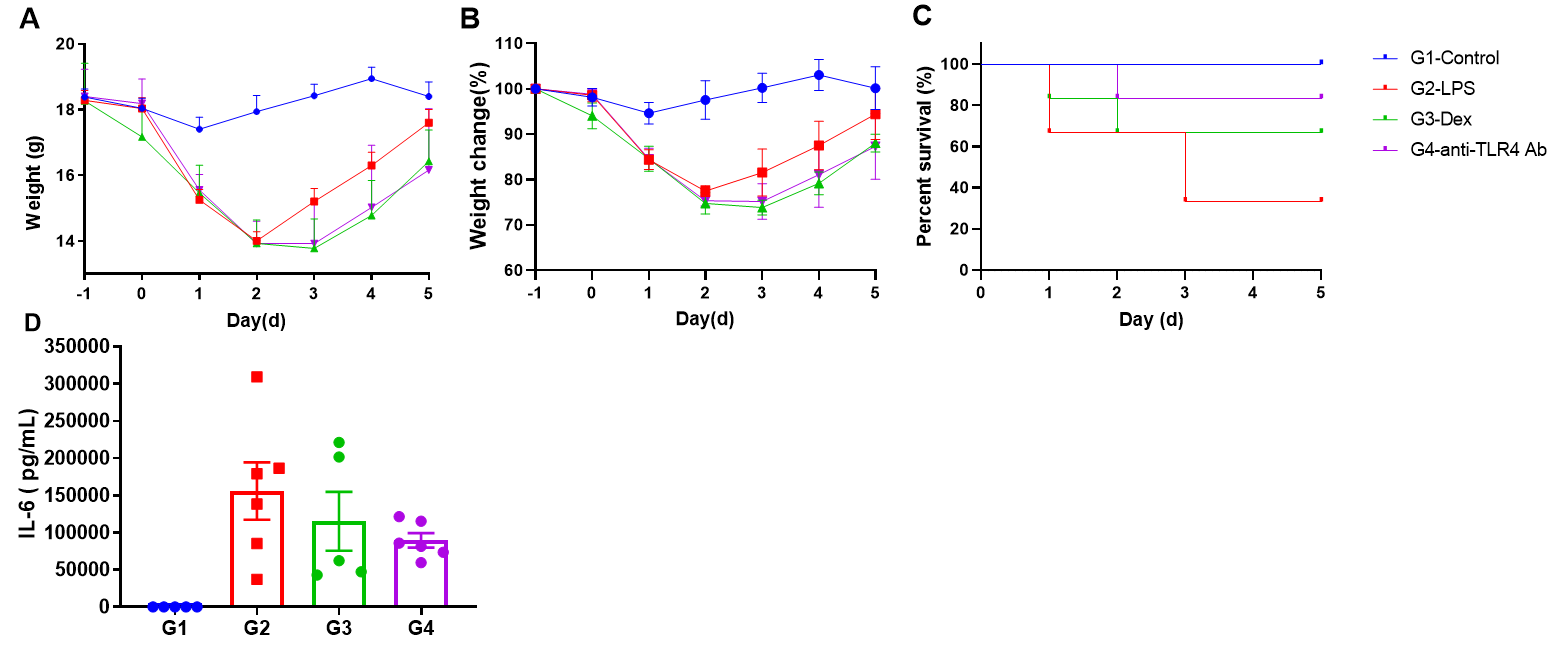
Effects of anti-TLR4 antibody on LPS-induced acute inflammation. (A) The body weight and (B) change of weight after LPS treatment; (C) The survival rate of LPS-induced acute inflammation mouse model was rescued and (D) the level of IL6 in serum after Dex and anti-TLR4 Ab treatment was significantly decreased in LPS-induced acute inflammation.

References
[3] Hwang JS, Kim KH, Park J, Kim SM, Cho H, Lee Y, Han IO. Glucosamine improves survival in a mouse model of sepsis and attenuates sepsis-induced lung injury and inflammation. J Biol Chem. 2019, 294(2):608-622.
[4] Evans CE, Peng Y, Zhu MM et al. Rabeprazole Promotes Vascular Repair and Resolution of Sepsis-Induced Inflammatory Lung Injury through HIF-1α. Cells. 2022, 11(9):1425.






 +86-10-56967680
+86-10-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn