



Flow cytometry assay is performed on animal tissues collected after in vivo drug administration, and the fluorescence signal detected after direct incubation with anti-human IgG secondary antibody is used as the bound receptor signal. Following supersaturated incubation of the corresponding test samples, anti-human IgG secondary antibody is added and then the detected fluorescence signal is used as the total receptor signal.
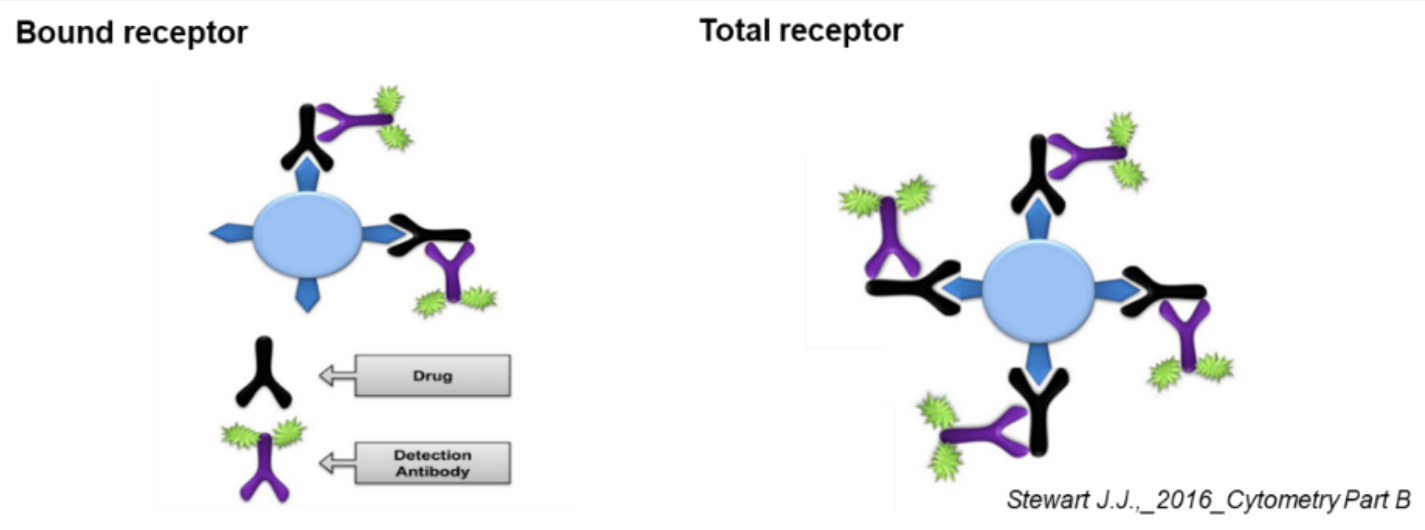
RO% = ((MFI of Tareget cells)bound -(MFI of Tareget cells)control) /
((MFI of Tareget cells)total -(MFI of Tareget cells)control) × 100%
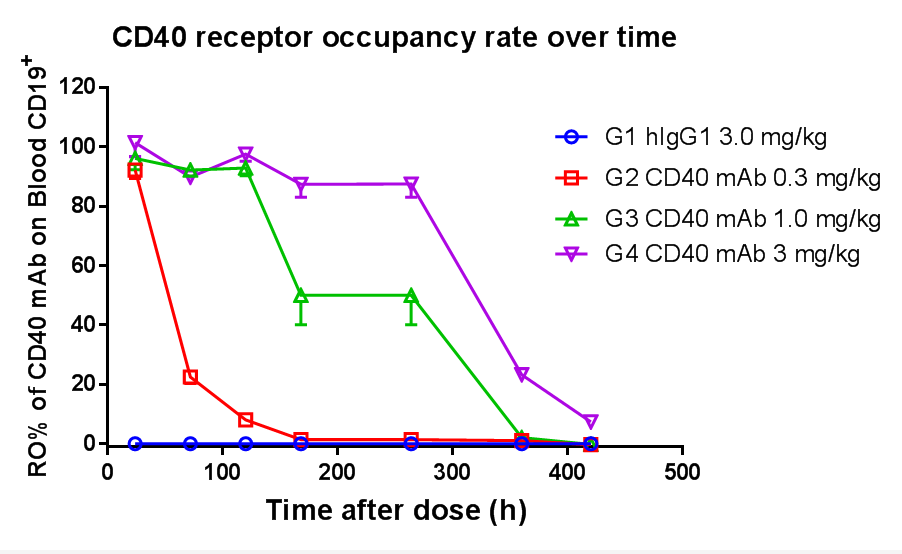
Receptor Occupancy Assay of CD40 Antibodies on CD19+ B Cells in Peripheral Blood of B-hCD40 Mice
Flow Cytometry
Overview: Flow cytometry uses an integrated system of fluidics, optics, and electronic detectors to detect various microsomes based on their fluorescence and physical properties. It is a technique that effectively differentiates heterogeneous cell populations at the single cell level.
Test objects: Suspension cells, adherent cells, or single cell suspensions prepared by isolation from solid tissues (organs or tumors).
Principle: Single cells are lined up to pass through the laser irradiation zone in sequence, and a series of optical detectors collect the scattered light and fluorescence signals from the cells.
Applications: Cell counting, cell sorting, fluorescent biomarker detection, etc.
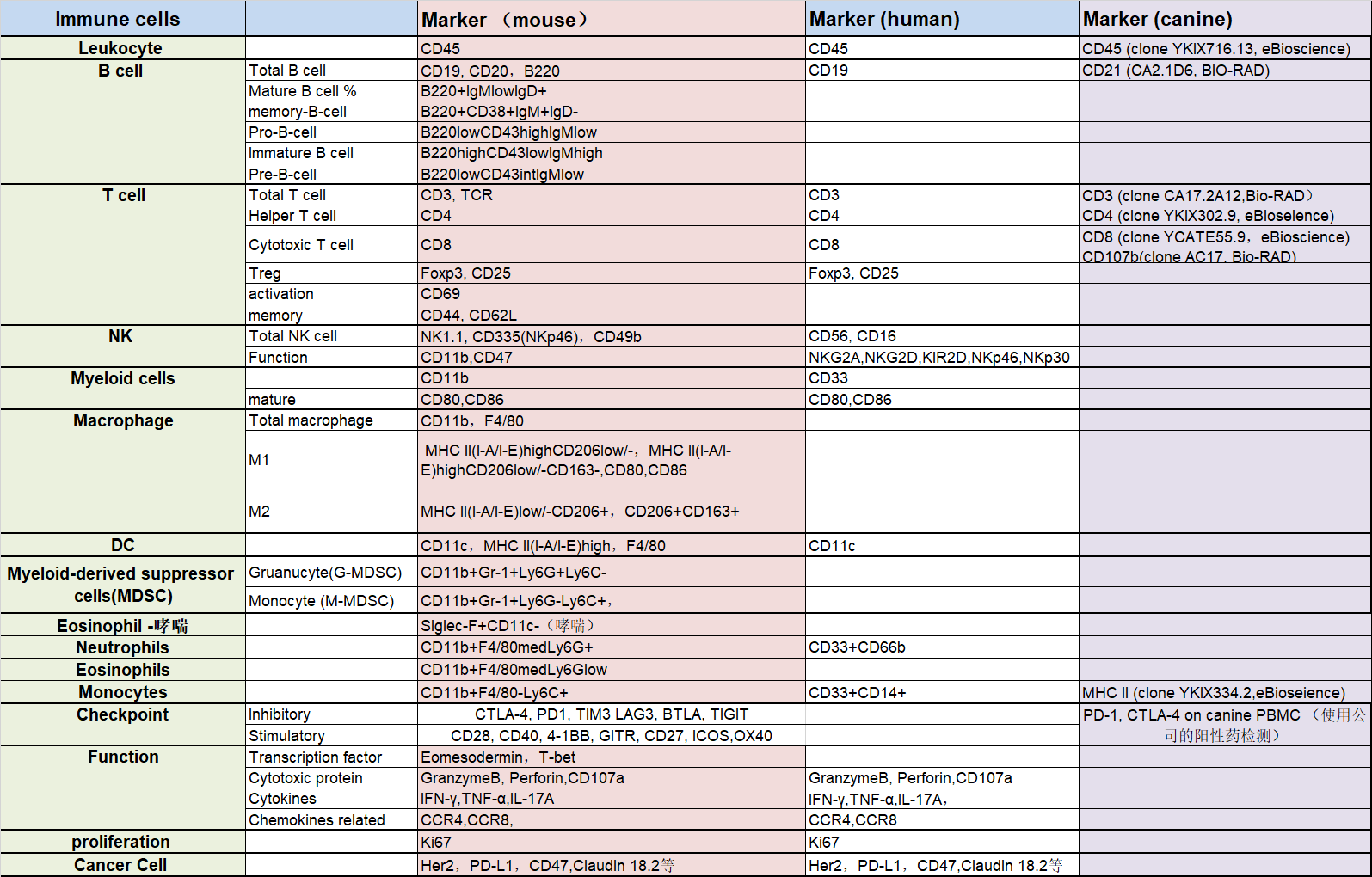
Common Markers for Flow Cytometry Assay
Multicolor Immunofluorescence (IF) of Tissue In Situ
IHC
Principle: Based on the principle of specific binding between antigen and antibody, the antigen (polypeptide and protein) in tissue cells can be determined by chemical reaction with antibody labeled by chromogenic agents (fluorescein, enzyme, metal ion, and isotope). The study to localize and analyze antigen qualitatively and quantitatively is called immunohistochemistry or immunocytochemistry.
RNA Scope
Principle: Tissue sections (FFPE) are first properly pretreated and then the target RNA is hybridized with specific oligonucleotide probes with ACD proprietary. The RNAscope® 2.5 HD Duplex Chromogenic Assay employs two independent signal amplification systems, each using a different chromogenic enzyme to react with substrate for color development. Two target RNA transcripts are shown in two different colors as dots or clustered signals which are visible at 40–100× magnification under bright field microscope.
Flow Cytometry
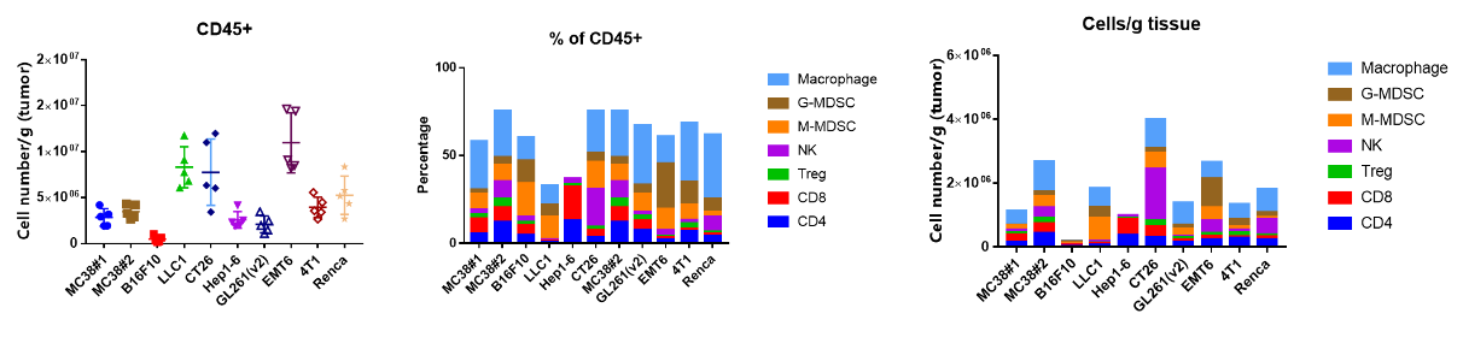
Common Homologous Tumor Model TIL Assay
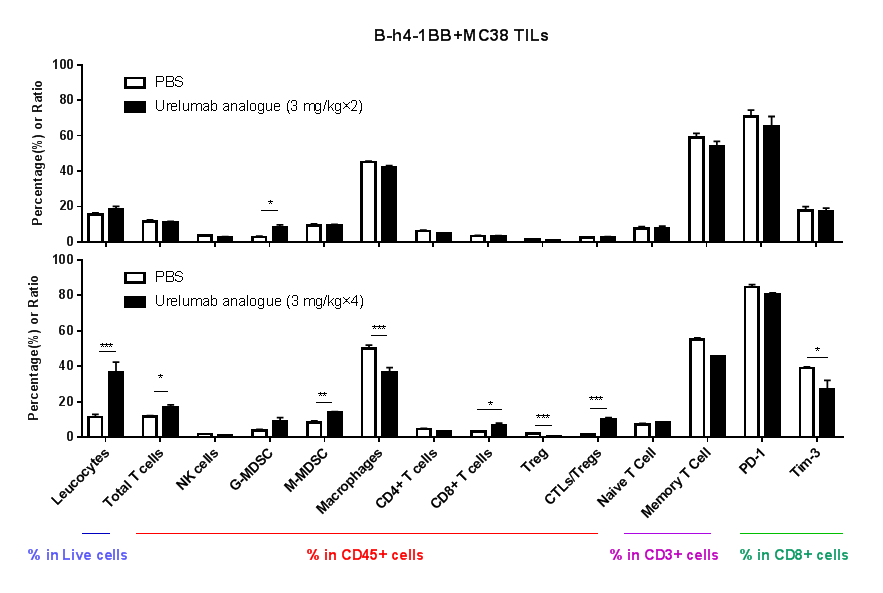
Immune-Related Analysis of 4-1BB Antibody in Tumor Efficacy Evaluation
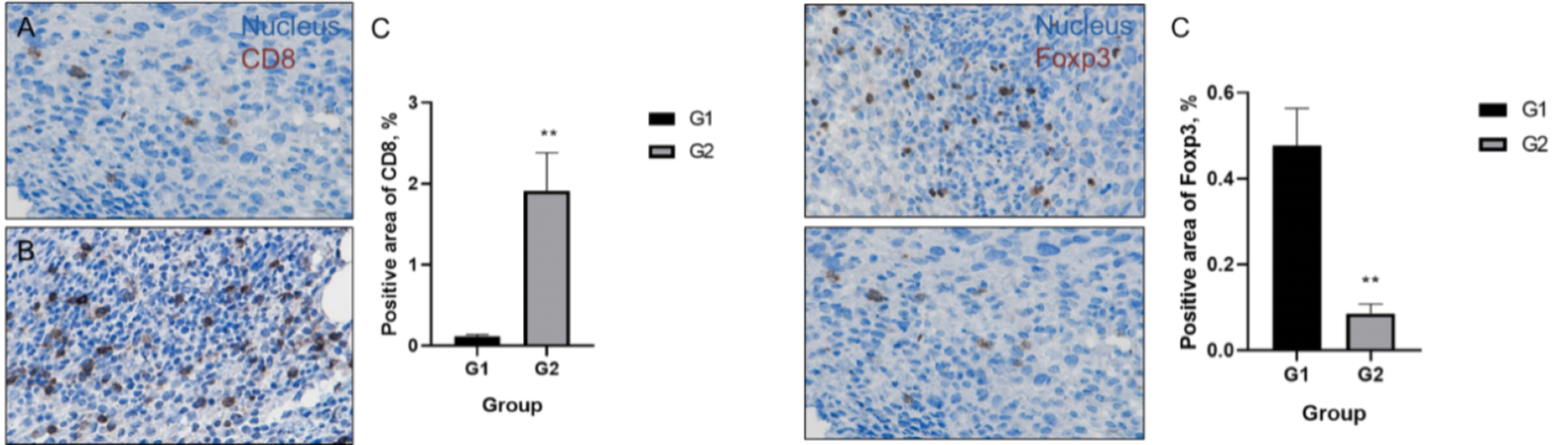
Humanized 4-1BB, B-h4-1BB mice subcutaneously implanted with MC38 tumors were intraperitoneally administered with Urelumab. Immune analysis of tumor tissues:
No significant changes were observed in various immune cell subpopulations after two administrations of the test article;
After four administrations, Urelumab analogue induced an increase in tumor-infiltrating immune cells including CD8+ T cells, and a decrease in Treg cells, which led the tumor microenvironment to the active status of killing tumor cells.
Tissue In Situ Multi-color Immunofluorescence
Principle: A technique to determine antigen/antibody localization by labeling antibodies/antigens with fluorescent tags
Workflow: Paraffin section --> dewaxing to water --> antigen repair --> blocking --> labeled antibody staining/primary antibody staining --> DAPI staining of nuclei/secondary antibody staining --> HRP/fluorescent staining --> DAPI staining --> sealing and observation
Throughput: 24 slices per time
Tissue: immune organs (spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, etc.), intestines, tumors, etc.
Co-staining: 8 colors (including DAPI), 4 colors (including DAPI)
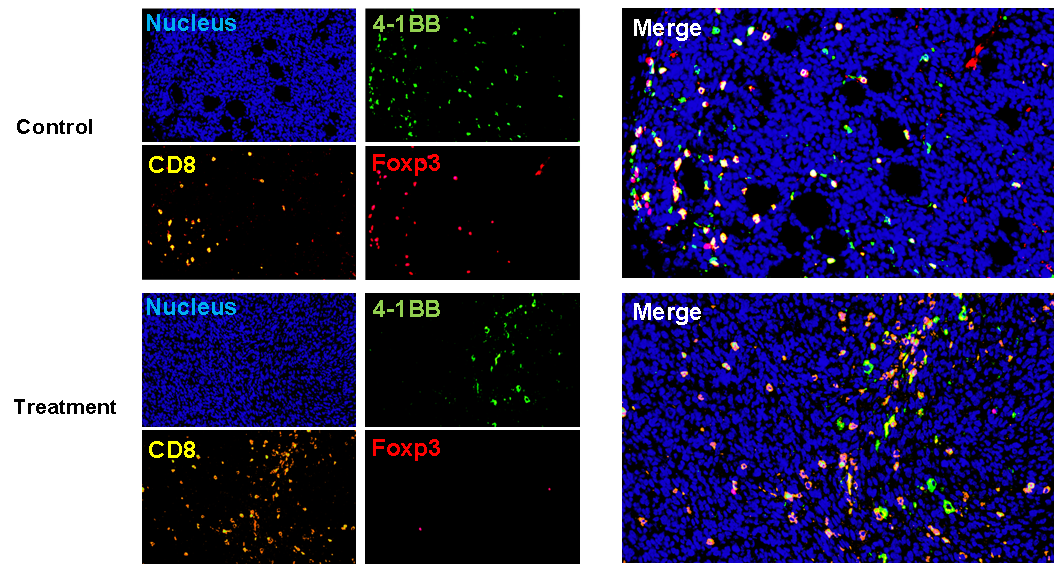
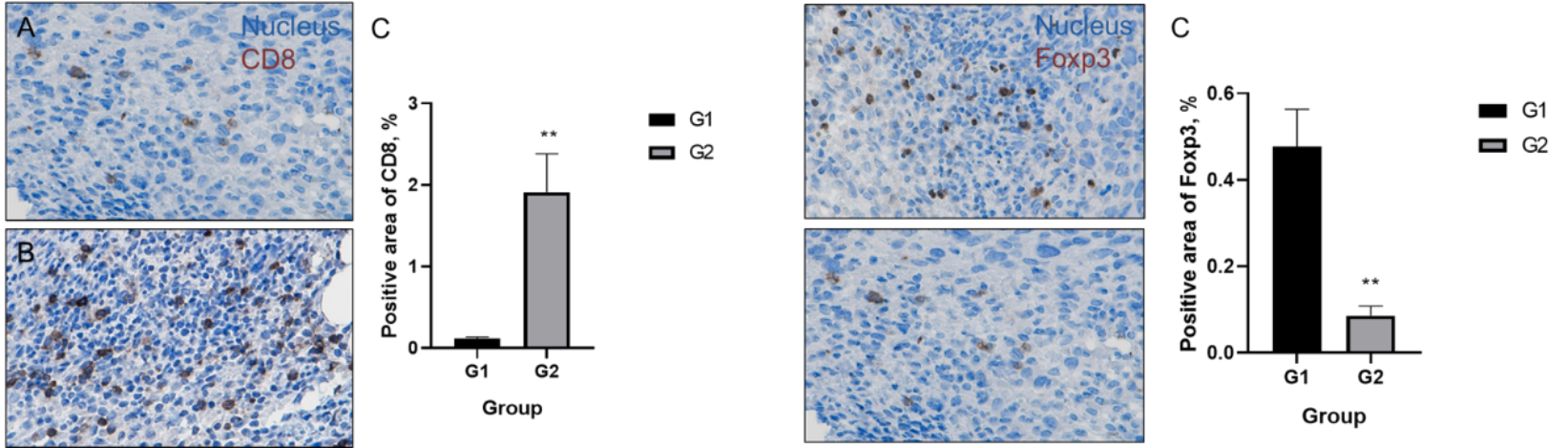
Tumor Microenvironment Evaluation — TILs
RNA Scope
Principle: Tissue sections (FFPE) are first properly pretreated and then the target RNA is hybridized with specific oligonucleotide probes with ACD proprietary. The RNAscope® 2.5 HD Duplex Chromogenic Assay employs two independent signal amplification systems, each using a different chromogenic enzyme to react with substrate for color development. Two target RNA transcripts are shown in two different colors as dots or clustered signals which are visible at 40–100× magnification under bright field microscope.
Cytokines are a group of low-molecular-weight soluble proteins produced by a variety of cells, including interleukins, interferons, chemokines, and tumor necrosis factors, which play important roles in modulating body's immune responses.
ELISA
Principle: The antigen and antibody bind to form a solid phase immune complex. The qualitative or quantitative analysis of antigen/antibody is carried out by the degree of color reaction between the added enzyme labeled antibody and the substrate.
Method:Double antibody sandwich (a common method for antigen detection): A solid-phase carrier is coated with specific antibodies to detect the antigen in the test sample.
Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) is a flow cytometry based quantification of multiple proteins. It integrates various features such as immune-beads, laser detection, signal processing, and computational calculation, and is capable of qualitative and quantitative analysis of multiple indicators in a sample. Compared with ELISA, the CBA assay features higher analyte capture efficiency, faster processes, and more accurate results, while using less sample.
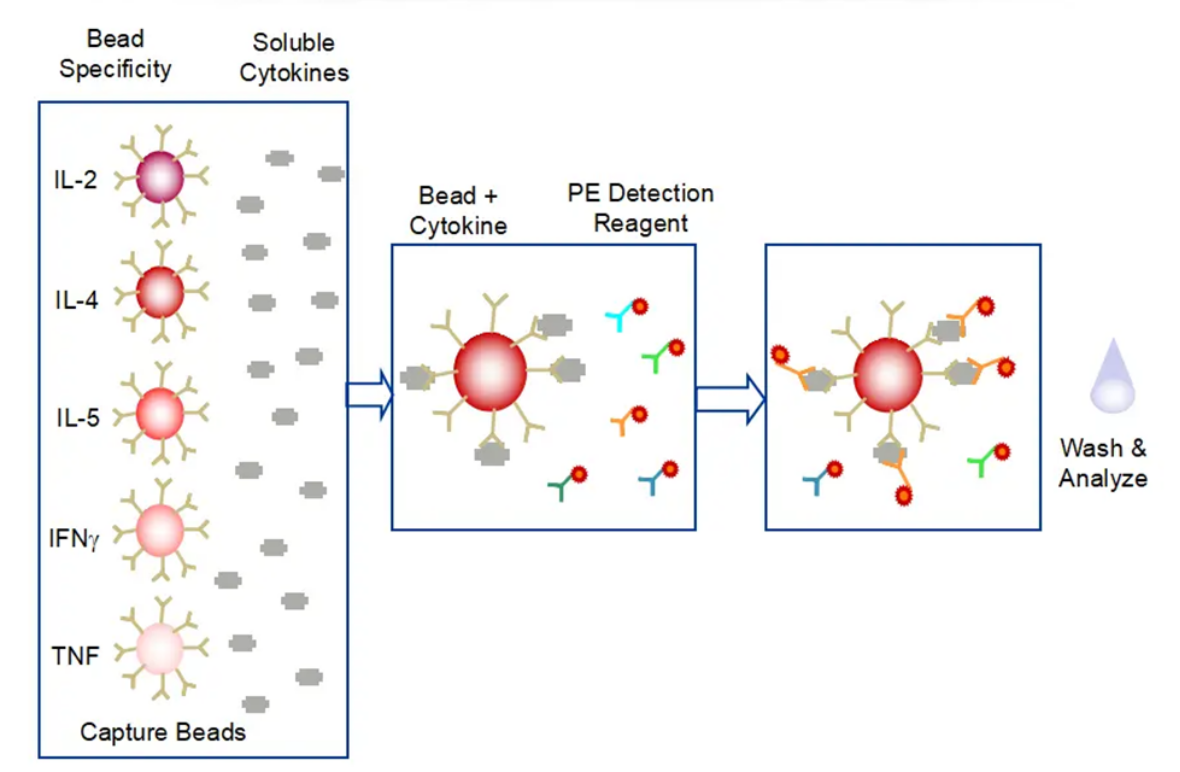
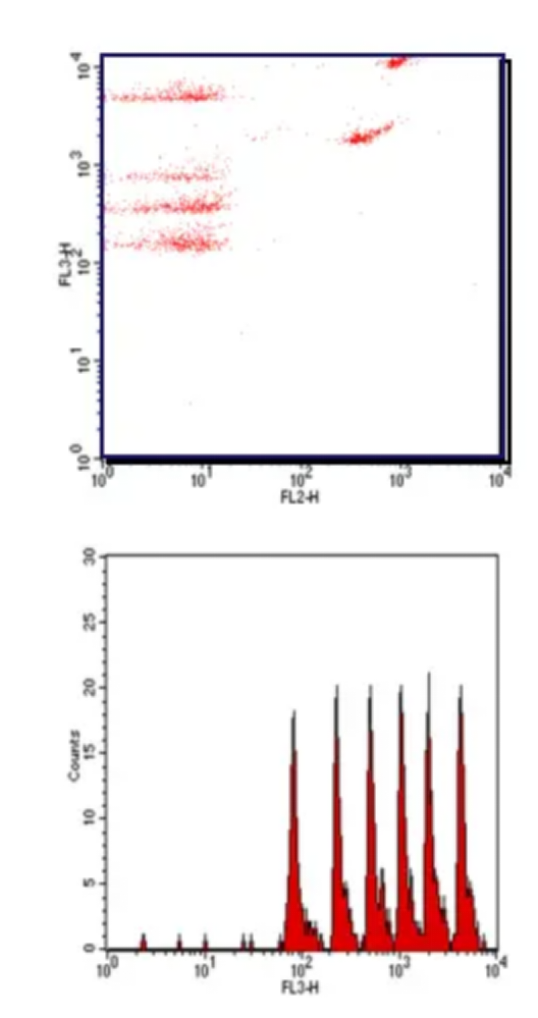
Case: Cytokine Profiling in B-hCD40 Mice
Cytokines are a group of low-molecular-weight soluble proteins produced by a variety of cells, including interleukins, interferons, chemokines, and tumor necrosis factors, which play important roles in modulating body's immune responses. CD40 is a costimulatory receptor expressed mainly in antigen presenting cells (APCs). Binding of its ligand CD154 (CD40L) expressed on T cells or binding of agonistic anti-CD40 antibodies results in the activation of both APCs and T-cells as well as the production of a variety of cytokines. Biocytogen has created B-hCD40 mice where the murine CD40 extracellular domain is replaced by human CD40. This B-hCD40 model has been validated in in vivo efficacy study using anti-human CD40 antibody selicrelumab in a murine MC38 tumor model (A, B). Multiplexed cytokine analysis in MC38/B-hCD40 model treated with other anti-human CD40 antibodies has indicated varied cytokine profiles for these antibodies (C). Given that cytokine-mediated toxicity is one of the important clinical safety considerations in CD40-based therapeutics development, cytokine profiling helps select efficacious anti-human CD40 antibodies with reduced cytokine-mediated toxicity.
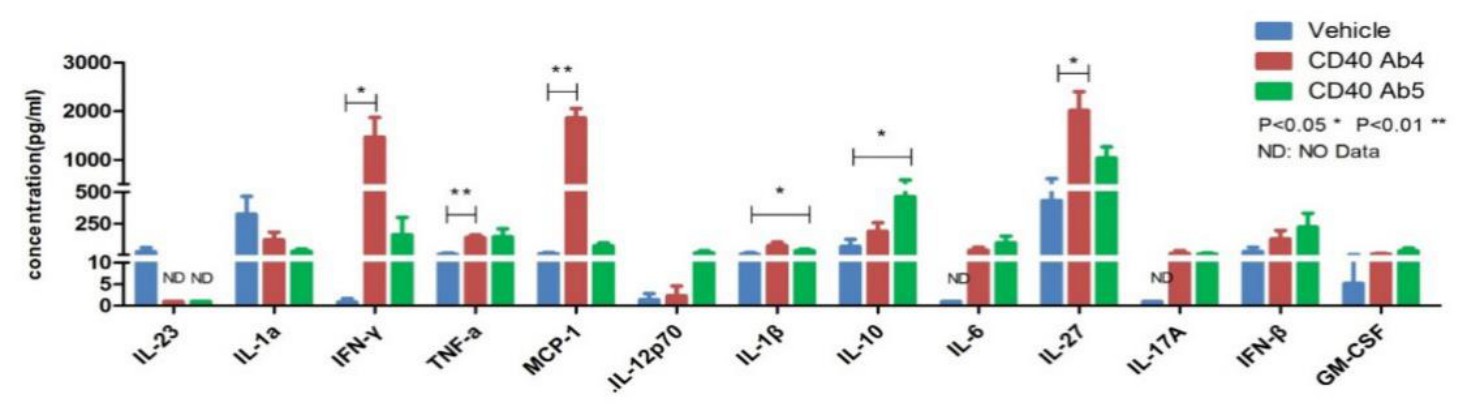
Changes in 13 cytokines in the serum of humanized CD40 mice injected with two different CD40 antibodies have revealed different levels of increase or decrease in cytokine secretion following the interaction with different antibodies.
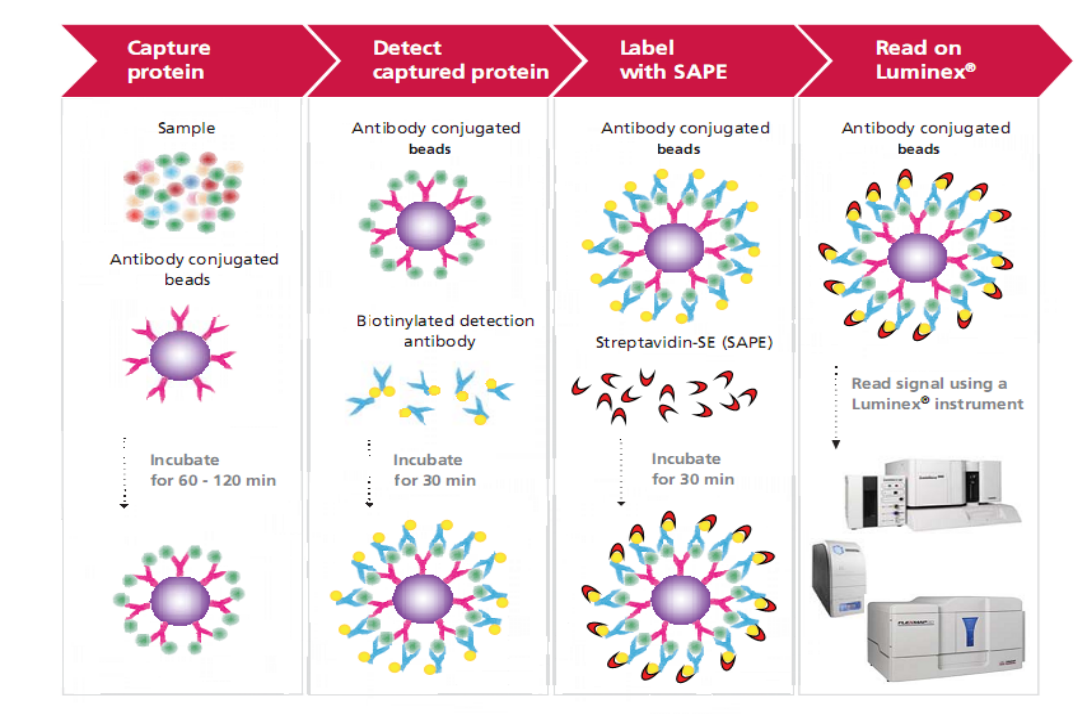
Luminex Multiplex Platform
Using a less sample volume, the Luminex® xMAP technology can simultaneously detect and quantify up to 500 factors, including cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, metabolic, endocrine and neurological indicators, antibody subtypes, and molecules related to tumors and signaling pathways. The technology employs differentially dyed capture beads for each target in a multiplex "ELISA-like" assay. Compared with traditional techniques (such as ELISA) for quantitative detection of liquid-phase sample indicators, the biggest advantage of this technology is that it can quantitatively and qualitatively detect dozens or hundreds of indicator molecules in a single sample at the same time.






 +86-10-56967680
+86-10-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn