
Background
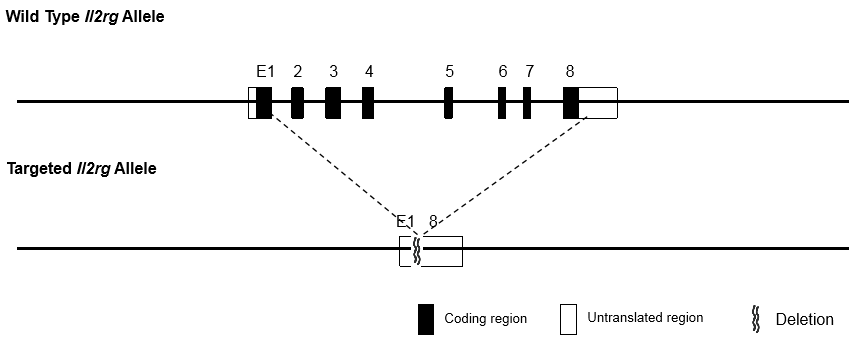
The Immune-deficient B-NDG mouse model (NOD.CB17-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1/Bcgen) was independently designed and generated by Biocytogen. B-NDG mice are generated by deleting the IL2rg gene from NOD-scid mice with severe immunodeficiency phenotype. Lacking mature T cells, B cells or functional NK cells, and displaying cytokine signaling deficiencies , this mouse model has the highest degree of immunodeficiency and thus is most suitable for engraft and growth of human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and human tumor cells or tissues.
• NOD-scid (non-obese diabetes, severe combined immunodeficiency) genetic background: mice of NOD genetic background and with Prkdc (protein kinase DNA-activated catalytic) knockout. Functional T cells, B cells and complement system in these mice are lost, and the activity of NK cells is greatly weakened.
• IL2rg null: the gamma chain of Interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R γc, also called CD132) is on the mouse X chromosome, and is the common receptor subunit of cytokines IL2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and IL-21 with important immune functions. After IL2r is knocked out, mouse immunity function is greatly weakened, activities of NK cells, which are almost completely lost.
• Prkdc null (DNAPK, scid): Prkdc (protein kinase DNA-activated catalytic) null mutation is characterized by significantly deficient of functional T cells and B cells, and an absence of lymphocytes, recapitulating severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) in human patients.
Major Applications
• Human-derived cell or tissue engraftment
• Tumor and tumor stem cell research
• ES and iPS cell research
• Hematopoiesis and immunology studies
• Human infectious disease studies
• Development of humanized models

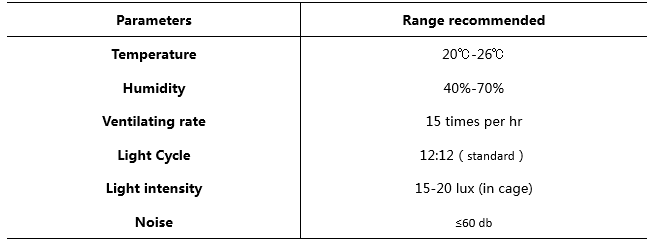
Animal breeding and maintenance
B-NDG mice are housed in isolators instead of IVCs in our facility. Based on our experience, the mice can live up to 2 months in SPF standard IVCs. This time frame matches the requirements of most experiments performed with B-NDG mice. To improve facility standards, strict sanitation procedures are recommended: cages and bedding need to be sterilized by autoclaving or Co60 irradiation before use, and cages need to be changed in laminar flow hoods weekly. Keeping a clean, high standard housing environment helps to improve the life span of B-NDG mice.
Animal breeding and maintenance
Transportation
Biocytogen’s B-NDG mouse can be shipped using land and/or air. Although the courier is notified to handle the crate with care, stress response of mice during shipment is still inevitable. Although enough supply of water jelly and food will be provided in cages, increased metabolism and fecal excretion caused by the stress may result in dehydration and loss of body weight. General percentage weight loss due to shipment is ~10%. The percentage can be as high as 15% if the shipment procedure is longer and the cage is populated. Usually, the most of the lost body weight is regained (although cannot reach 100%) after 5-7 days of adaptive feeding (Labdiet food is recommended)).
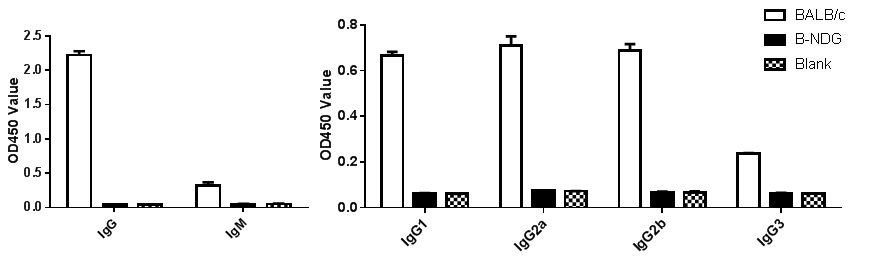
Phenotypic analysis
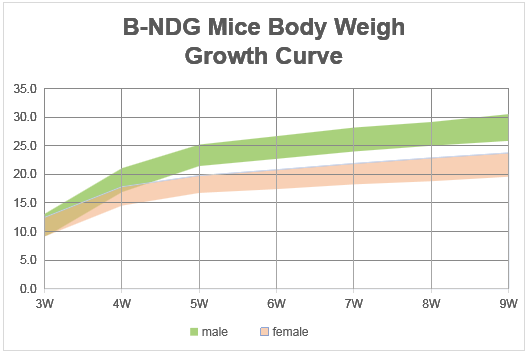
Body weight growth
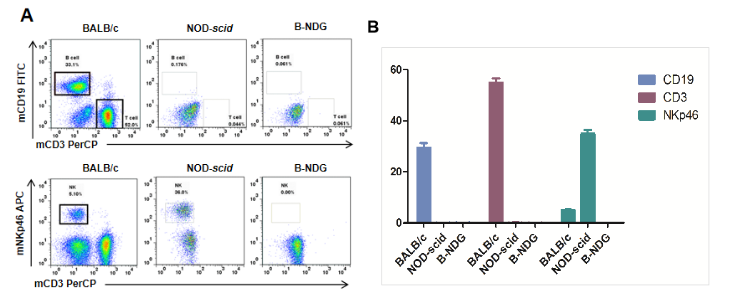
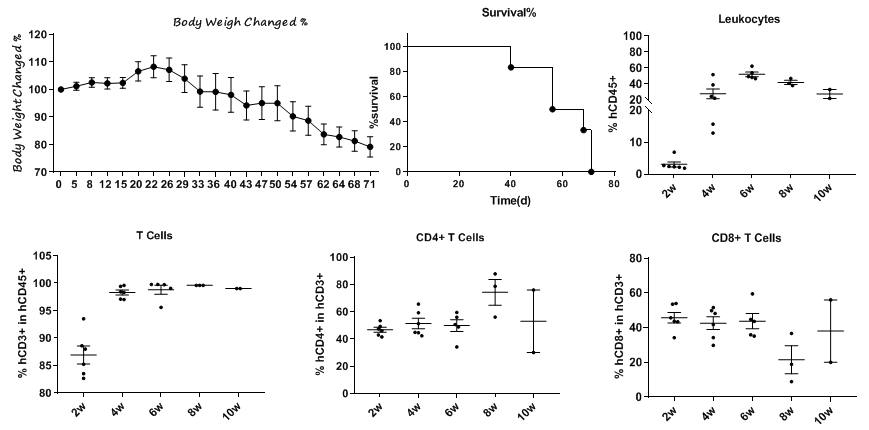
Flow-cytometric Analysis Using Specific Markers for T, B and NK Cells
Histology of spleen from B-NDG mice
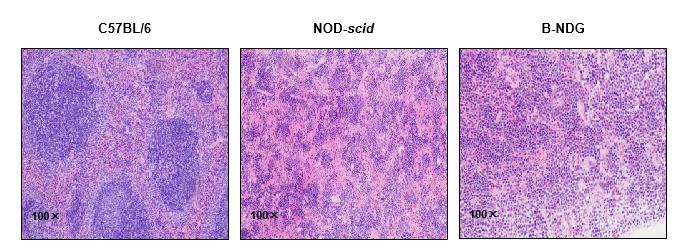
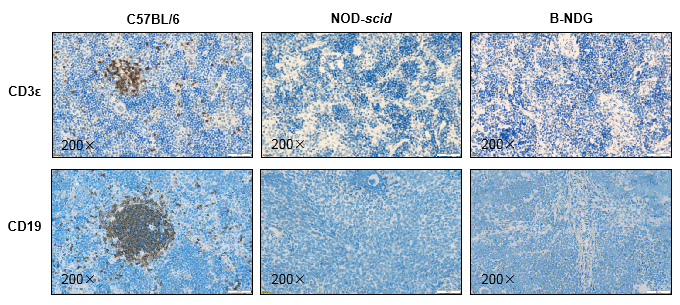
Figure 5. Histological sections of spleen from 9-week-old C57BL/6, NOD-scid, and B-NDG mice (n=3).
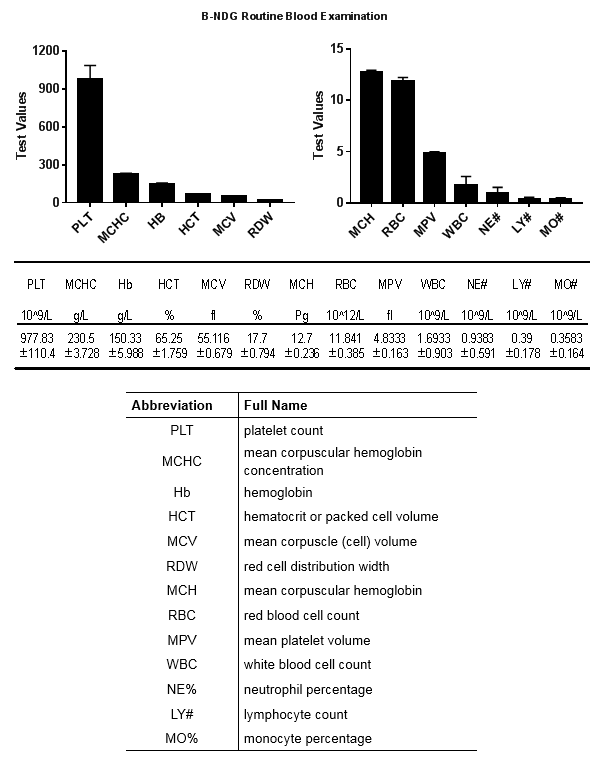
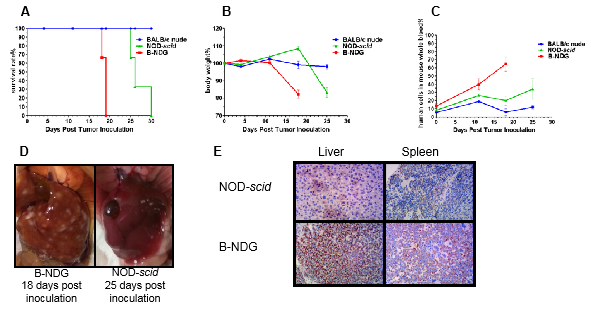
Figure 8. Raji B cells (5X106) were injected in to each B-NDG, NOD-scid and BALB/C Nude mice.
Drug in vivo efficacy study using Raji lymphoma CDX Tumor metastasis model in B-NDG mice.
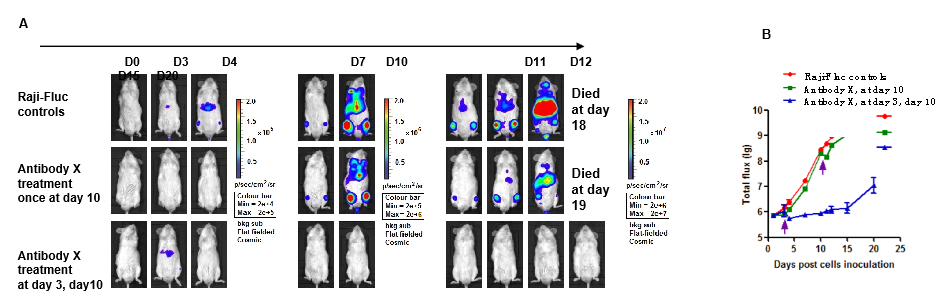
Figure 9. Raji-Fluc cells (5×105) were injected into B-NDG mice and the same dose of antibody X was given at day 3 and day 10. (A) In vivo imaging recorded at different time points to observe disease progression in mice. (B) Tumor curve for tumor cell fluorescence curves in different groups of mice. The effect of early treatment (at day 3, day 10) is remarkable, and this effect is significantly reduced for the late treatment (at day 10).
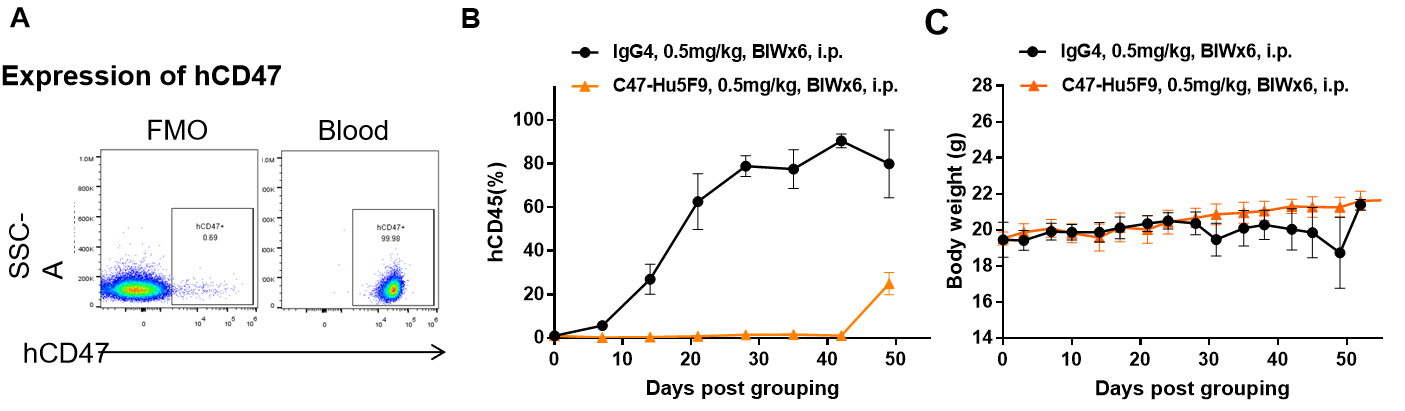
Human CD47 antibody in vivo efficacy study using Raji lymphoma CDX Tumor model in B-NDG mice.
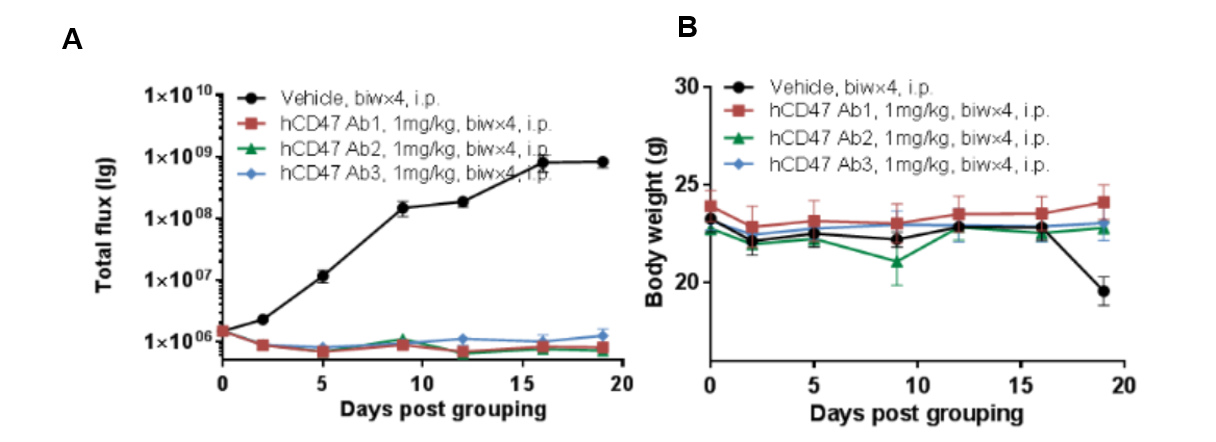
Human B-luciferase-GFP Raji cells (B lymphocytes) were caudal vein implanted into B-NDG. Mice were grouped when the fluorescence intensity reached approximately 1.0E+06 (n=6) at which time they were treated with anti-human CD47 antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (A) fluorescence imager was used to monitor tumor fluorescence in mice. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. The results showed that 3 antibodies had efficacies for tumor growth inhibition in B-NDG mice. B-NDG is a powerful model for human CD47 antibody efficacy study. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
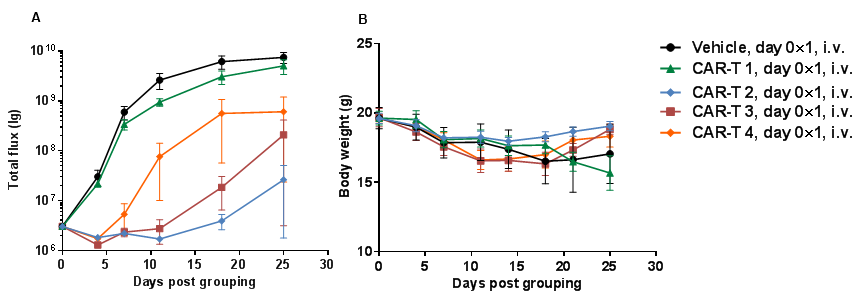
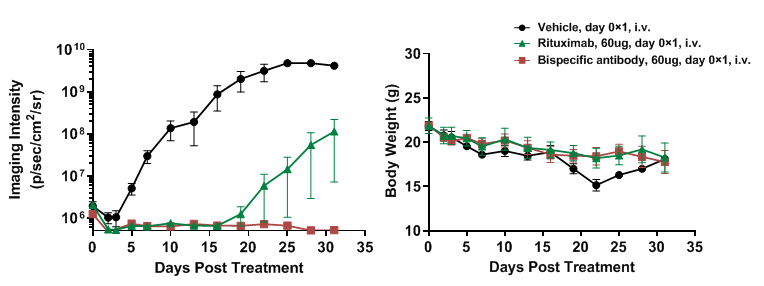
Human B-luciferase-GFP Raji cells (5E5), PBMC (5E6) and antibodies mixture were intravenously injected into B-NDG mice (n=4). (A) fluorescence imager was used to monitor tumor fluorescence in mice. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. Bispecific antibody shows significant inhibitory effects. The results indicate that establishing a CDX tumor model in B-NDG mice with reconstituted PBMCs provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Human Immune System Reconstituted Models and Efficacy Evaluation
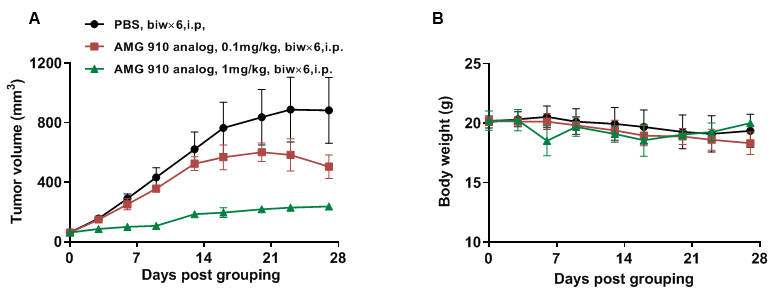
Figure 20. B-NDG mice reconstituted with PBMCs cells were used for CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody efficacy studies
NUGC4 cells (5E6) were subcutaneously implanted after human PBMCs (5E6) were intravenous implanted into B-NDG mice (female, 7 week-old, n=6). The animals were grouped into control and treatment when the tumor size was approximately 50-80 mm3 and the percentage of human blood hCD45% were above 10%, at which time they were treated with drugs. (A) Anti human CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody (AMG 910 analog) inhibited NUGC4 tumor growth in human PBMC reconstituted B-NDG mice. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. CD3×Claudin18.2 bispecific antibody shows significant tumor inhibitory effects. The results indicate that establishing a CDX tumor model in B-NDG mice with reconstituted PBMCs provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
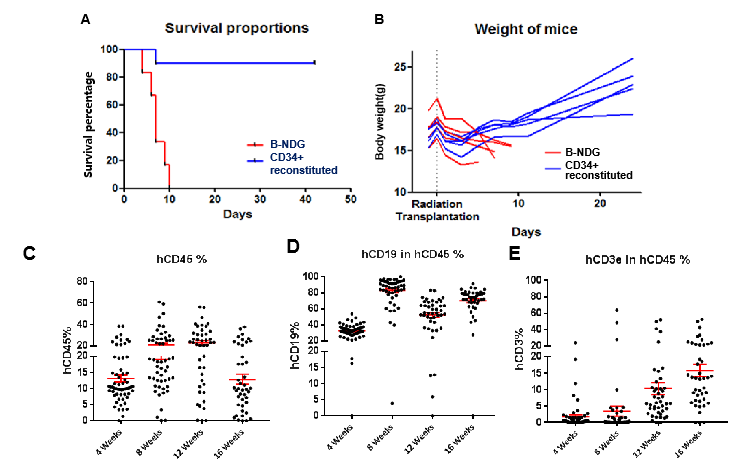
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have been game changers in tumor treatment during recent years. With improved therapeutic outcomes observed in a variety of solid tumors, this class of drugs has garnered considerable attention. Lacking of mature T, B, and NK cells, Biocytogen B-NDG mice are worldwide recognized as highly immunodeficient tool mice that are ideal for human cell or tissue transplantation. However, the defective immune system of the model itself makes it impossible to evaluate the efficacy of immunotherapy. Immunodeficient mice reconstituted with human immune cells offer a viable solution to this problem: human immune cells and hematopoietic stem cells are transplanted into B-NDG mice or B-NDG-derived mice to reconstitute their immune system, which can better simulate the human immune system for immunological studies and immune drug evaluation.
Biocytogen currently provides three immune reconstitution models: human peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) reconstitution, human hematopoietic stem cell (CD34+ HSC) reconstitution, and NK cell reconstitution. The immune reconstitution mouse model aids in the efficacy evaluation of immunotherapy drugs, bolstering the efforts in novel drug development and preclinical evaluation.

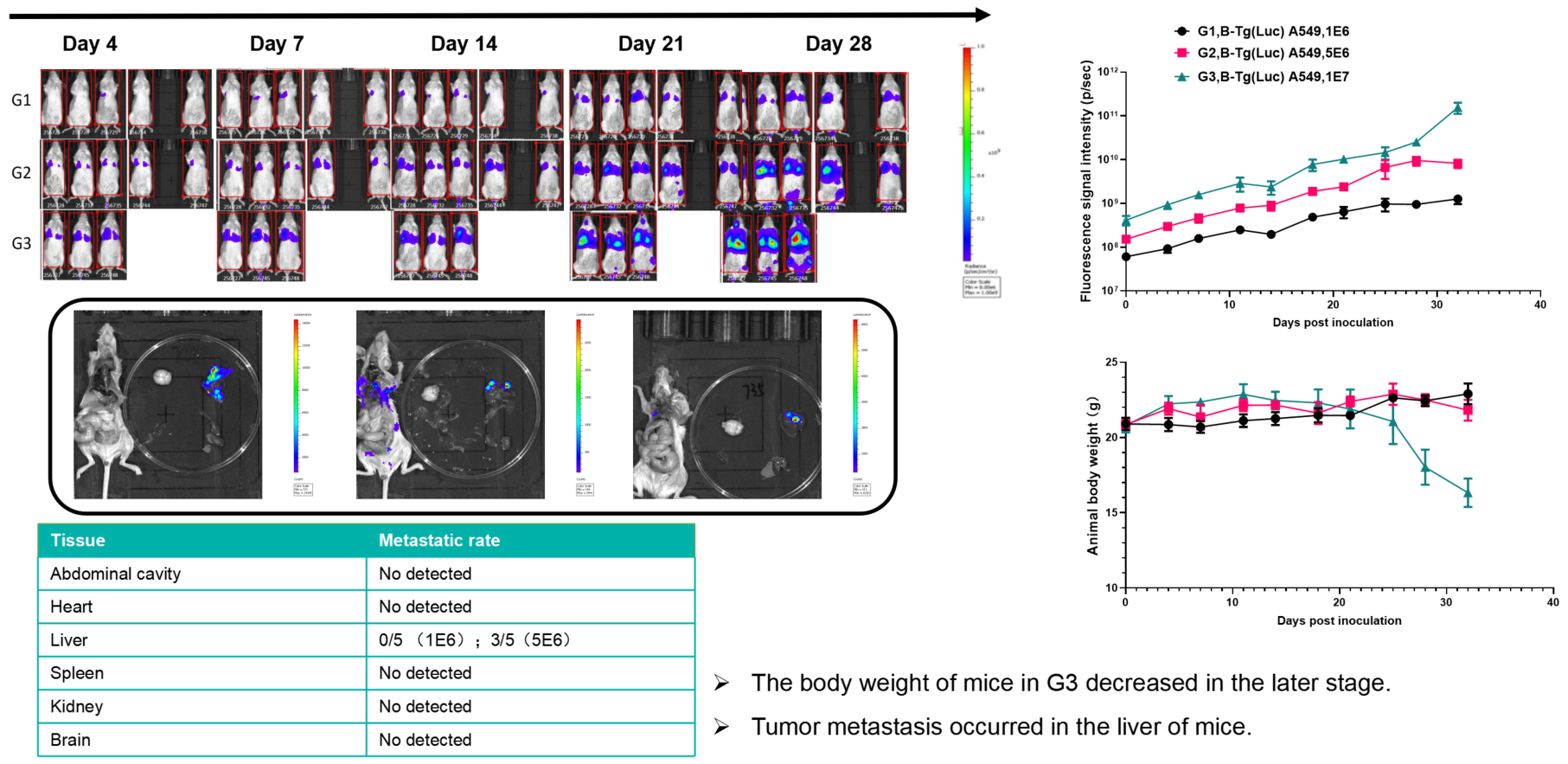
Lung cancer:B-Tg(Luc) A549(mix)+ B-NDG mice( i.v.)
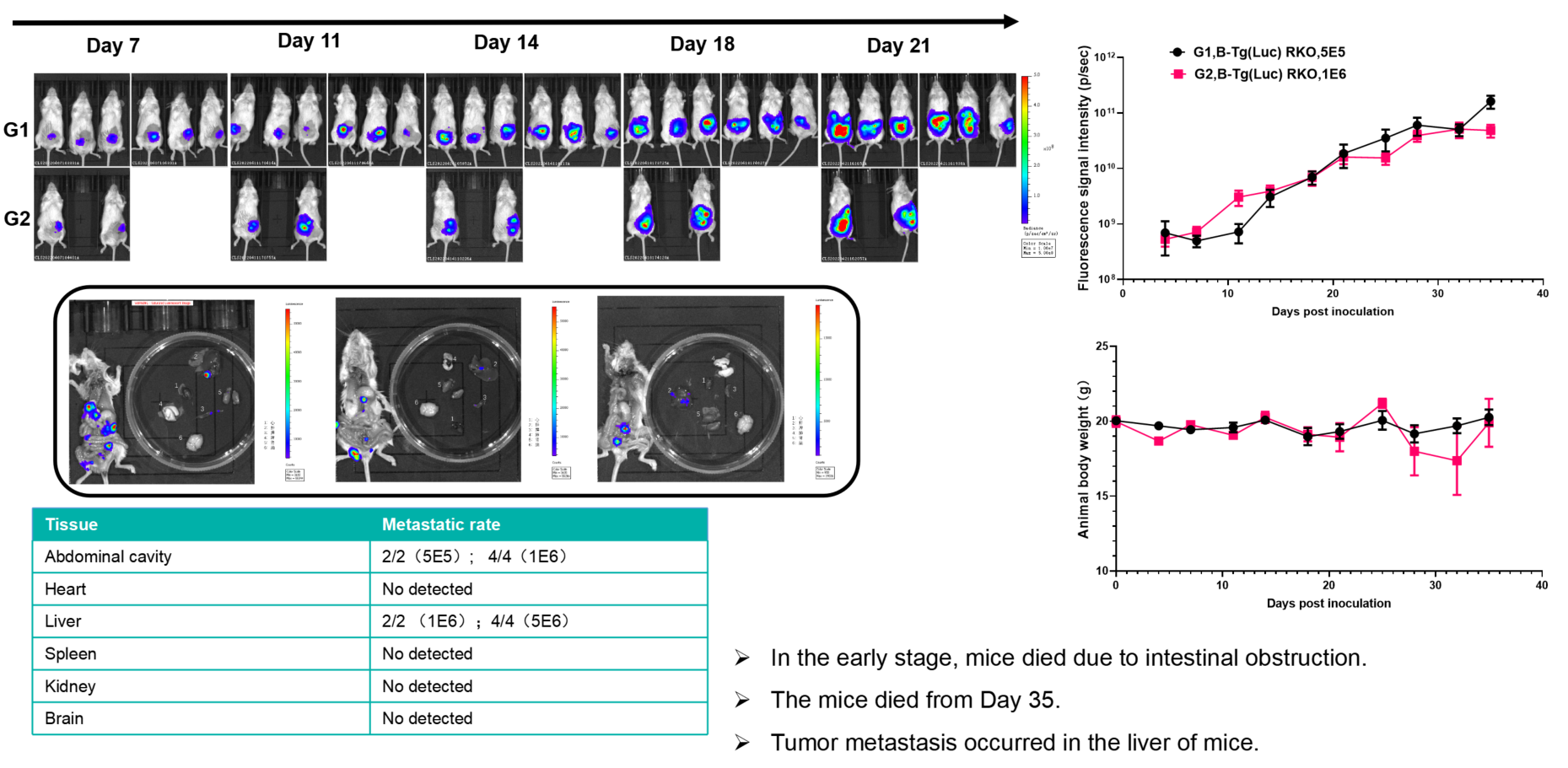
Colorectal cancer:B-Tg(Luc) RKO(mix)+ B-NDG mice(orthotopic)
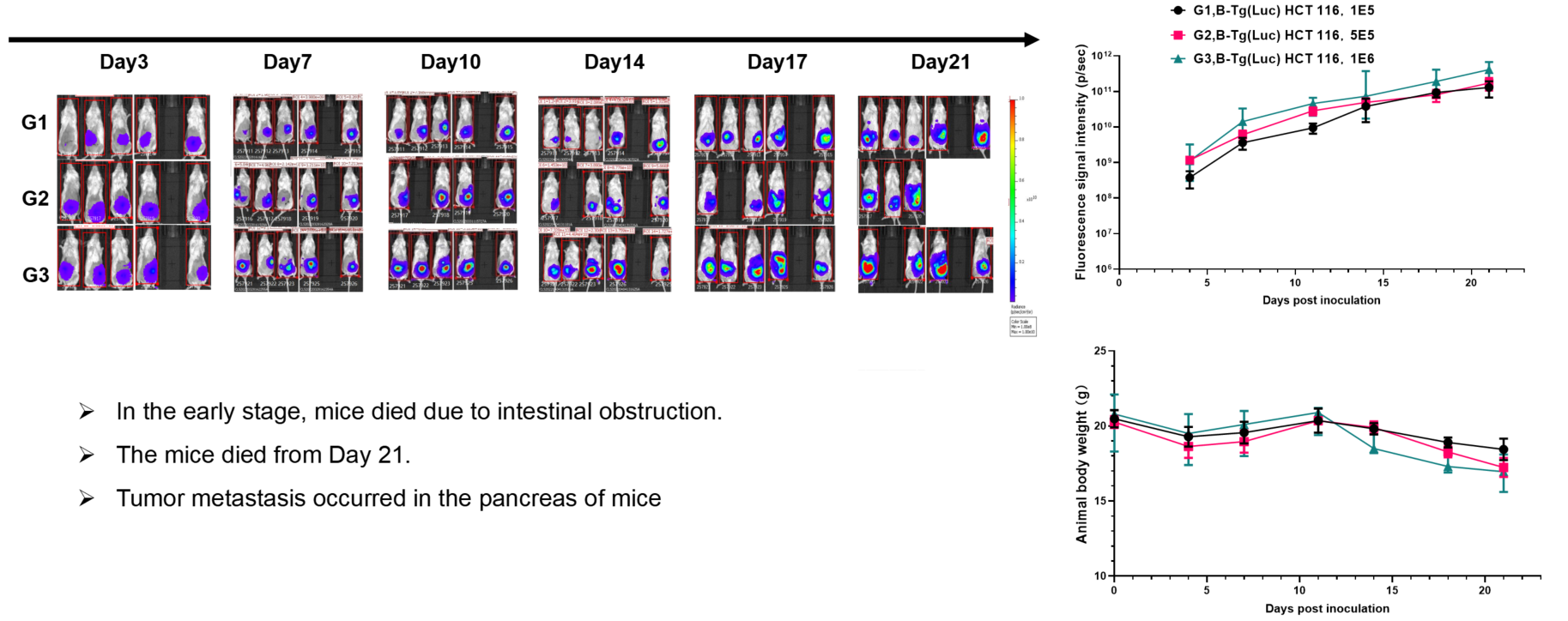
Colorectal cancer:B-Tg(Luc) HCT 116(mix)+ B-NDG mice (orthotopic)
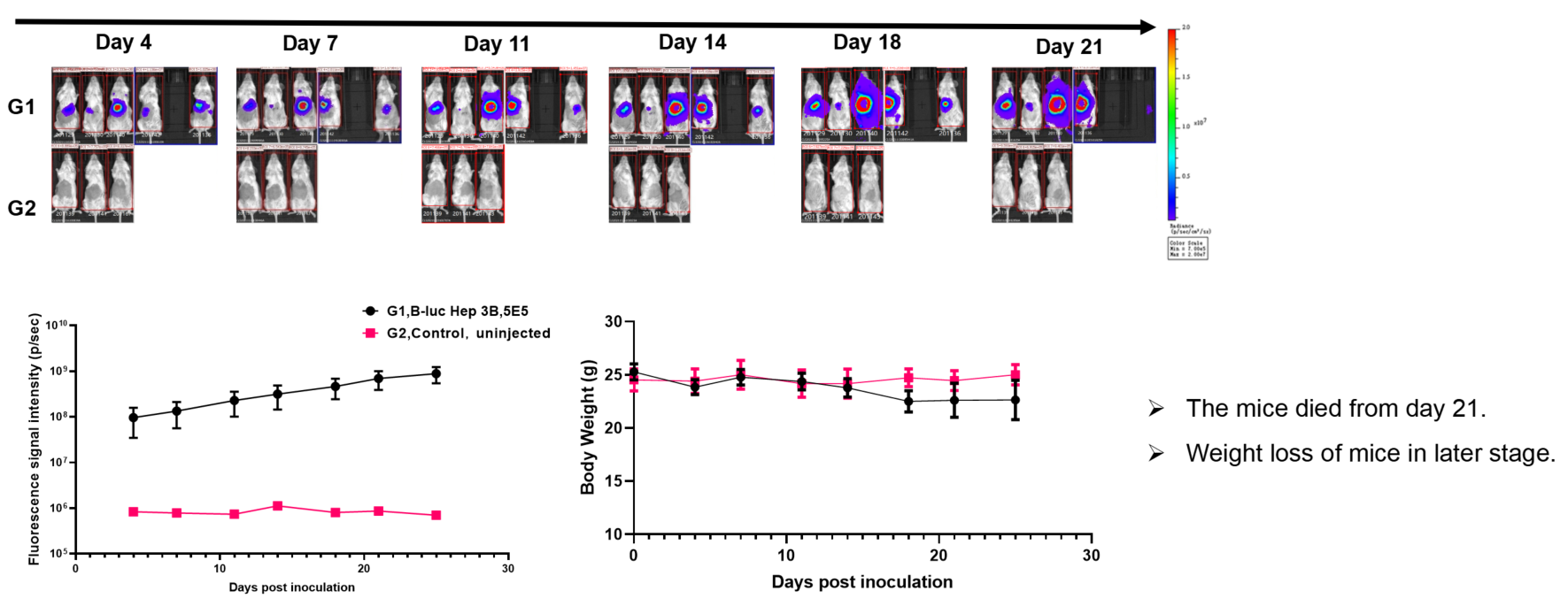
Liver cancer:B-luc Hep 3B plus + B-NDG hIL15 mice(orthotopic)
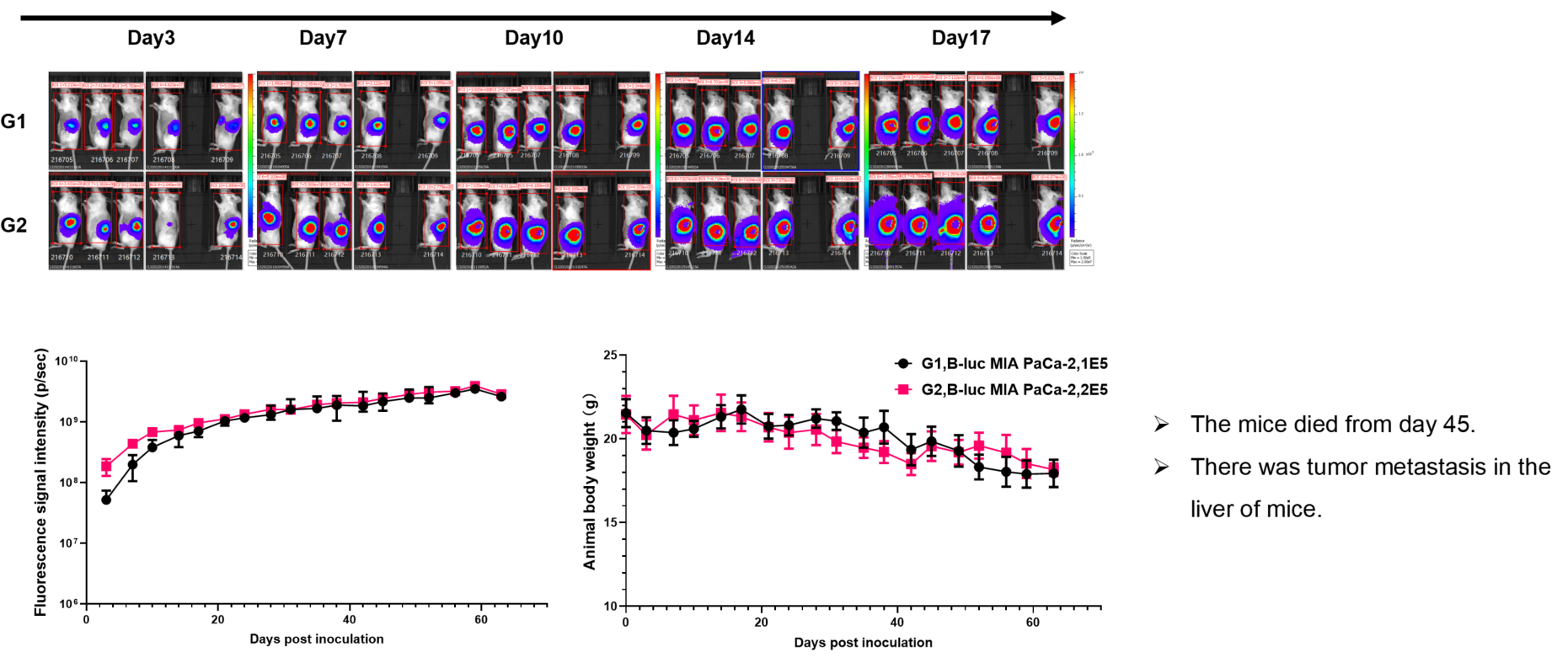
Pancreatic cancer:B-luc MIA Paca-2 #4+ B-NDG mice(orthotopic)
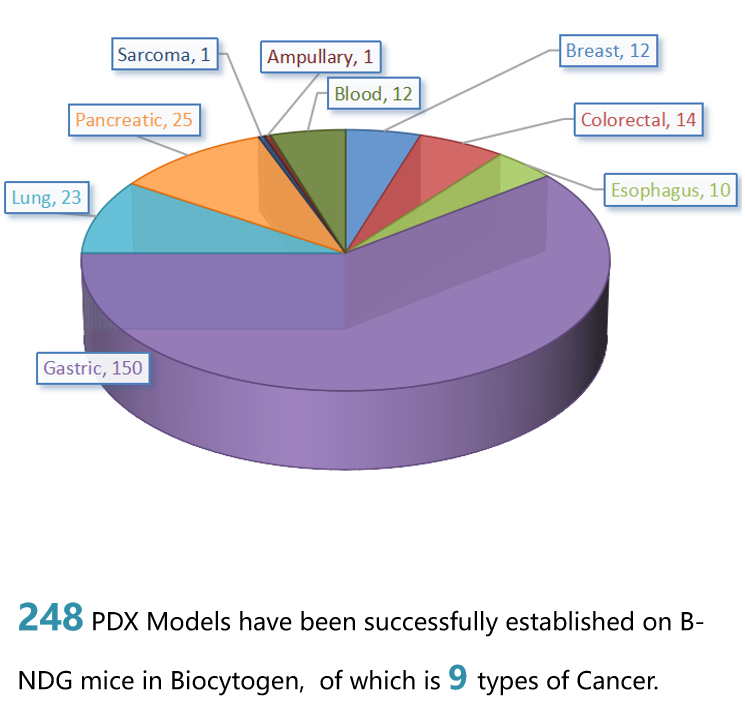
PDX Models are Successfully Established in B-NDG Mice
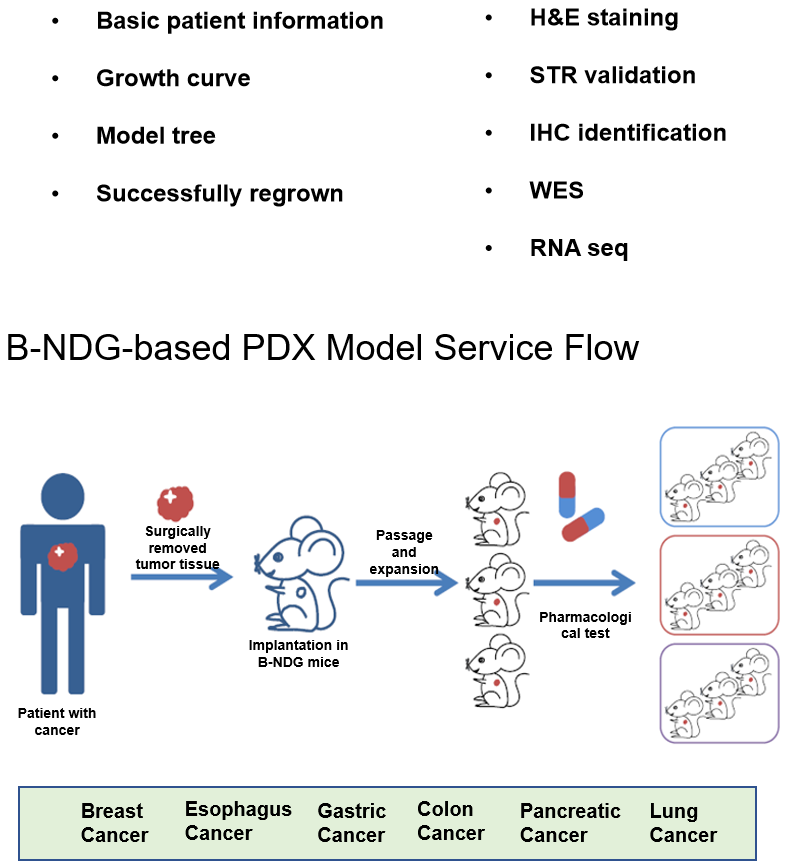
Efficacy evaluation of test articles in PDX models
1、Solid tumor of PDX
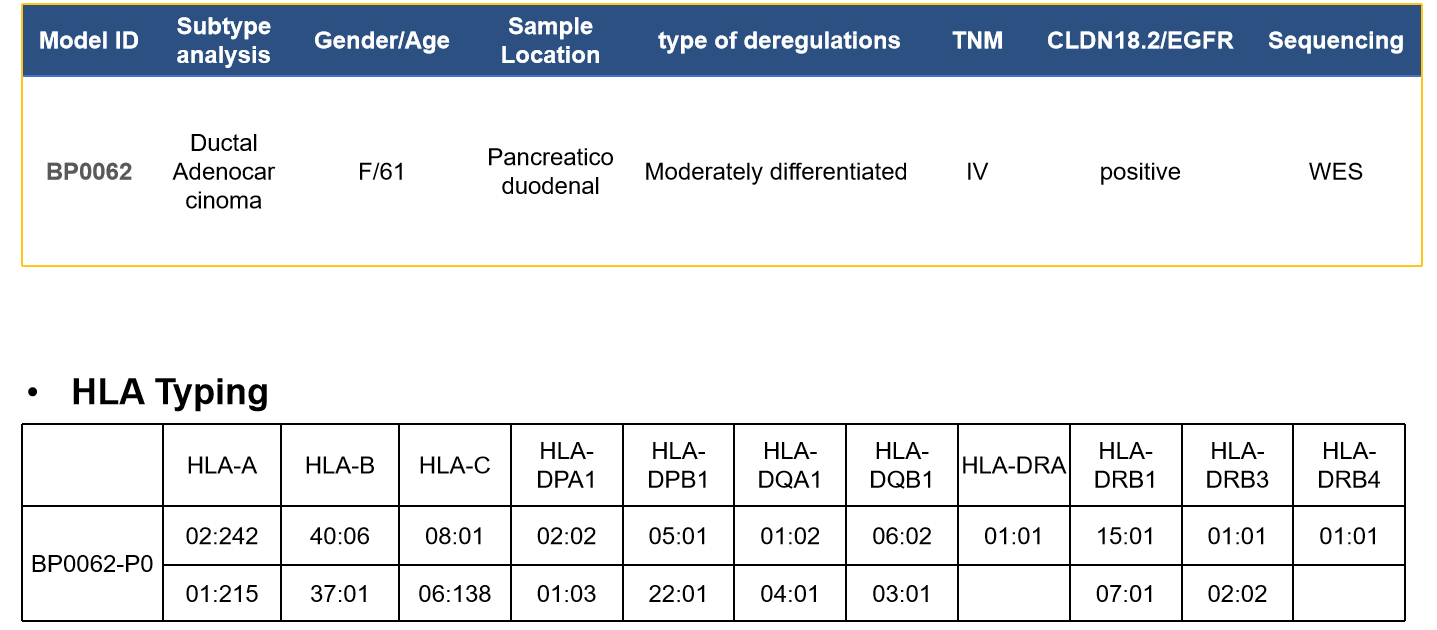
Case study:Pancreatic Cancer—BP0062
- Growth Curve in different passages of B-NDG mice
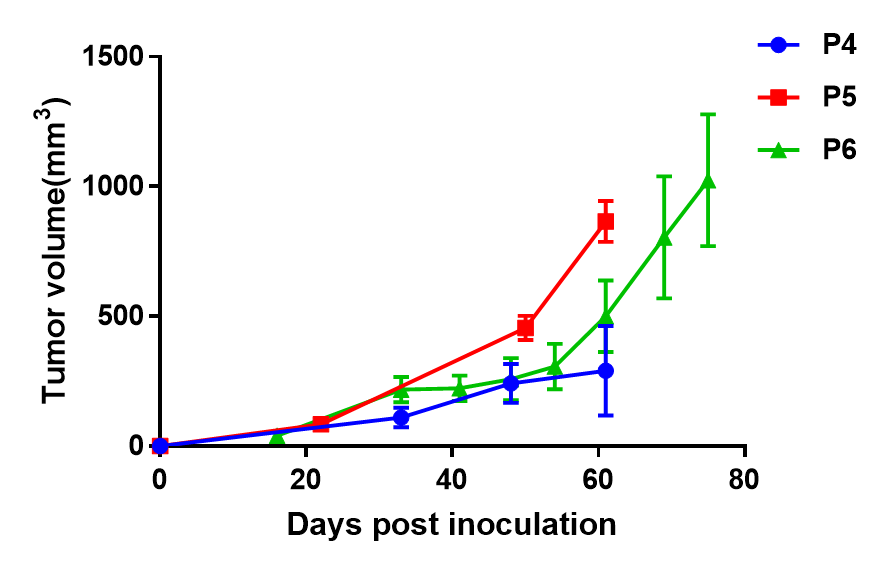
Results: The PDX model of Pancreatic cancer BP0062 is able to establish tumor model steadily in B-NDG mice and can effectively track tumor volume.
- Model Validation
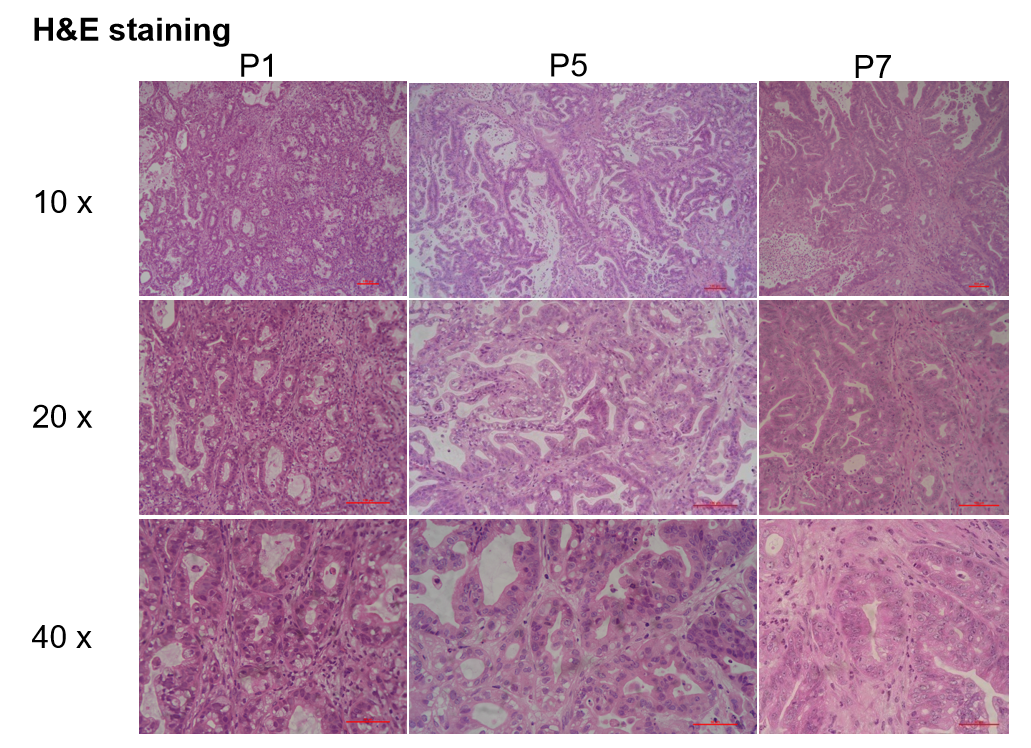
Patient-derived xenografts were found to recapitulate the structures in original patient samples and maintain similar heterogeneity in different generations.
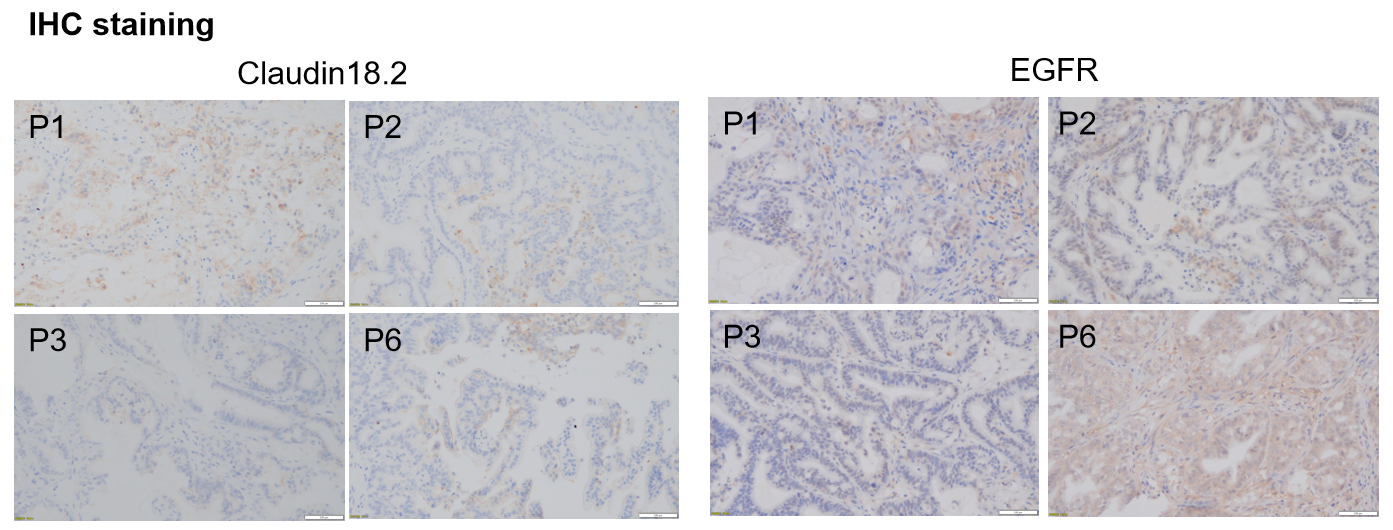
A thorough IHC assessment of CLDN18.2 and EGFR revealed no observable heterogeneity among individual turmous in different generations.
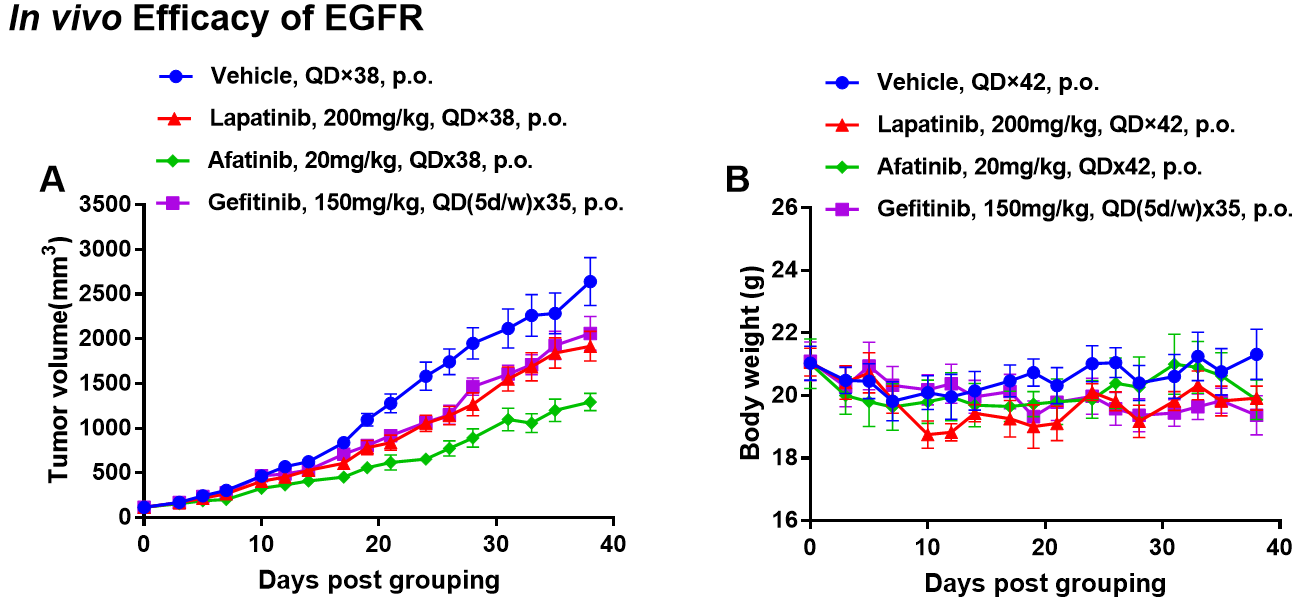
Antitumor activity of Drugs target EGFR in B-NDG mice . (A) Molecular targeted small-molecule anti-cancer drugs slightly inhibited tumor growth of BP0062 in B-NDG mice. PDX model of BP0062 was subcutaneously implanted into B-NDG mice (female, 6 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with different targeted drugs and schedules indicated in panel (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, Molecular targeted small-molecule anti-cancer drugs were efficacious, demonstrating that PDX model of BP0062 can be used to establish tumor model and provide a powerful preclinical pancreatic tumor model with EGFR positive cells. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
- Response of different mice strains in the same PDX models
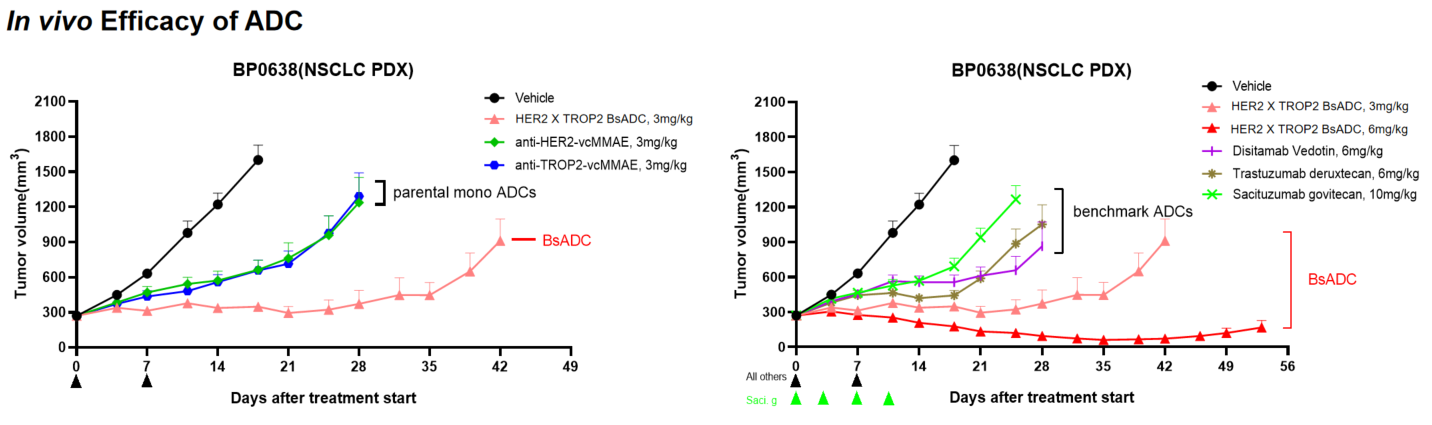
- In Vivo Efficacy: HER2 X TROP2 BsADC Showed Potent Anti-Tumor Activity in HER2-low PDX Models

2、LeukemiaPDX
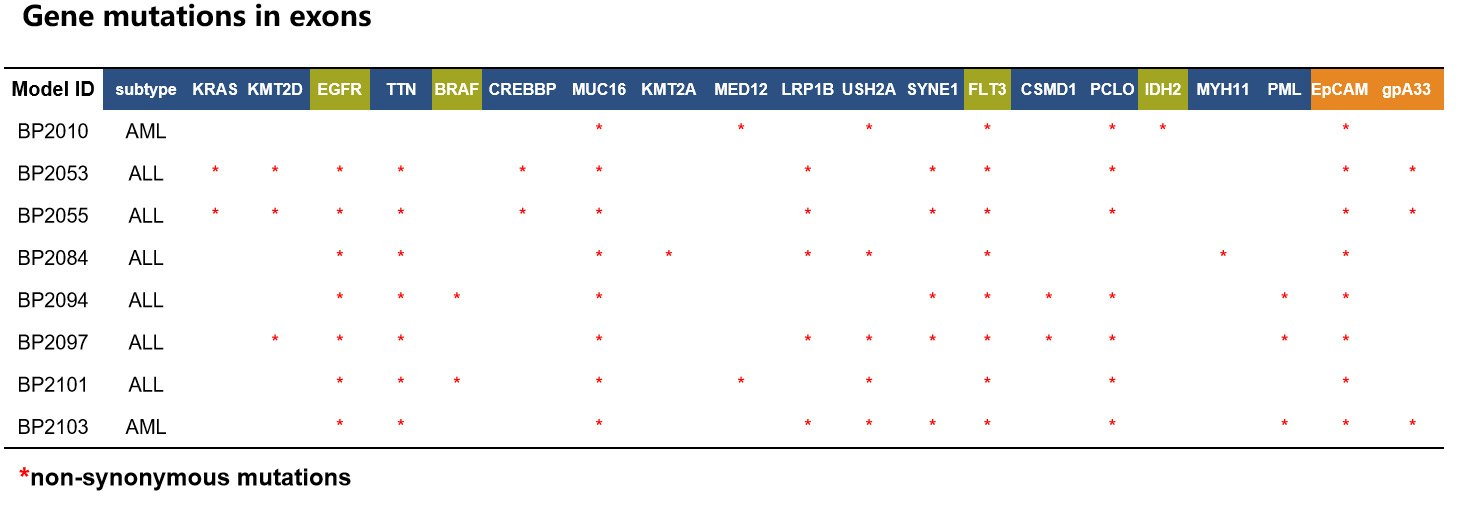
Case study:Leukemia PDX—BP2010
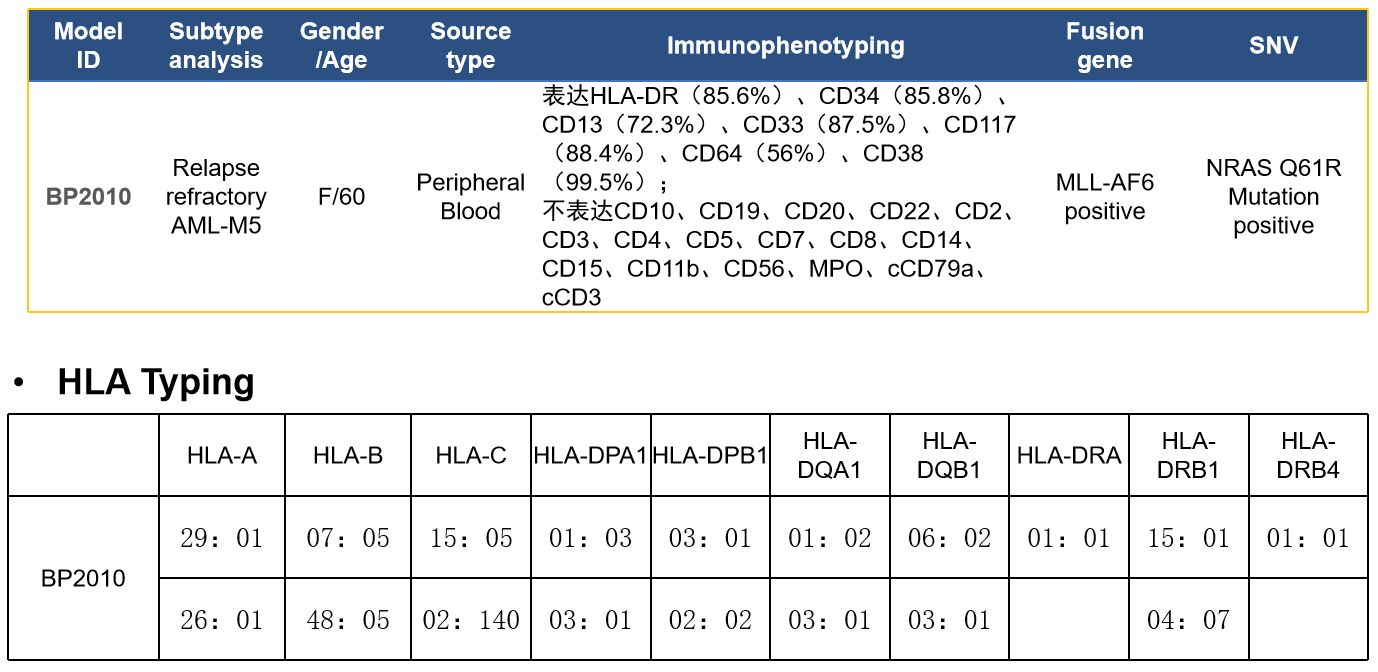
- WES(Whole Exome Sequencing) Examples
- Growth Curve in different strains of mice
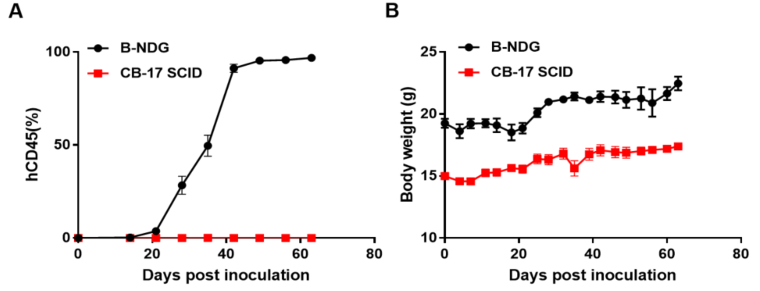
BP2010 was inoculated into CB-17 SCID mice via caudal vein. Tumor growth and mice body weight were measured twice a week. Tumor was analyzed by flow cytometry (n=10). (A) Tumor average growth ± SEM, (B) Mice average weight ± SEM
Results: The PDX model of leukemia PDX BP2010 is able to establish tumor model steadily in B-NDG while can not grow in CB-17 SCID.
- In vivo Efficacy of Chemotherapy
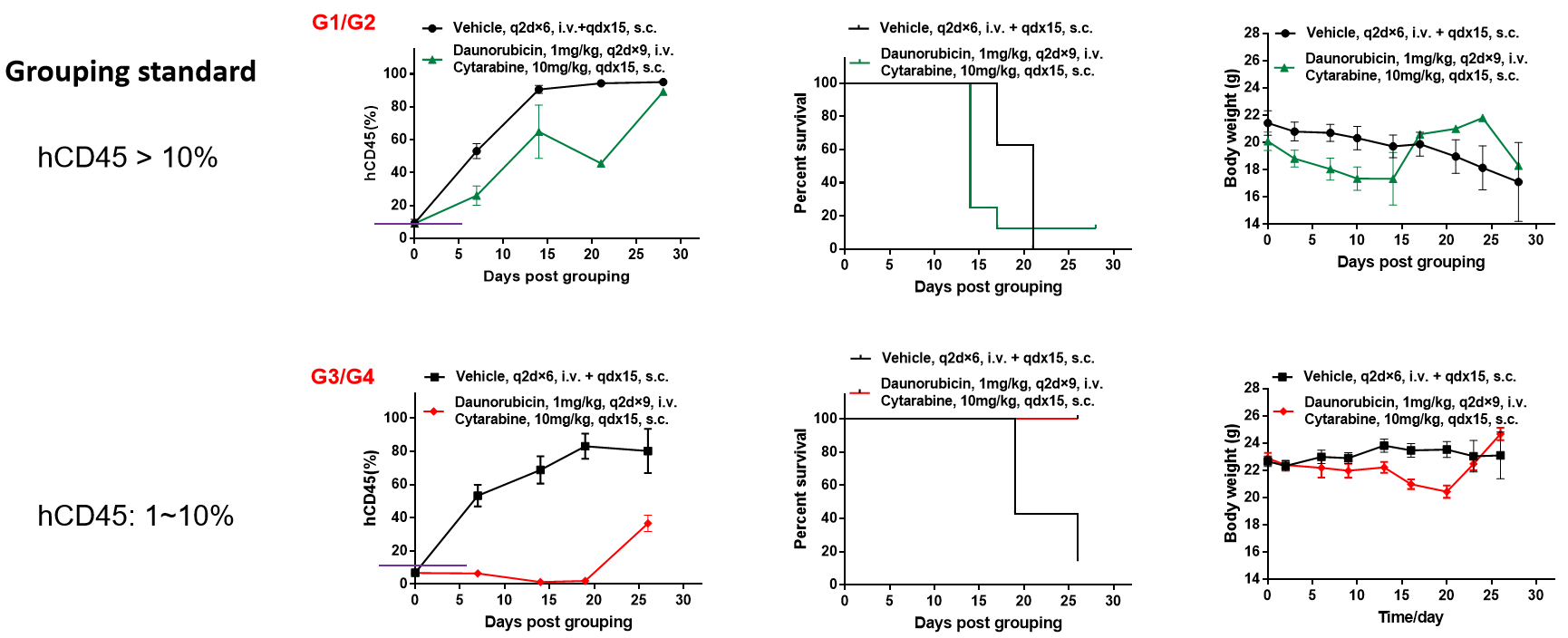
When hCD45 > 10%, the group was administered, and the treatment had no significant effect; when 10% > hCD45 > 1%, the group was administered, and the tumor inhibition effect was significant.
Conclusion: The degree of modeling during administration has a greater impact on the efficacy of small molecule drugs.
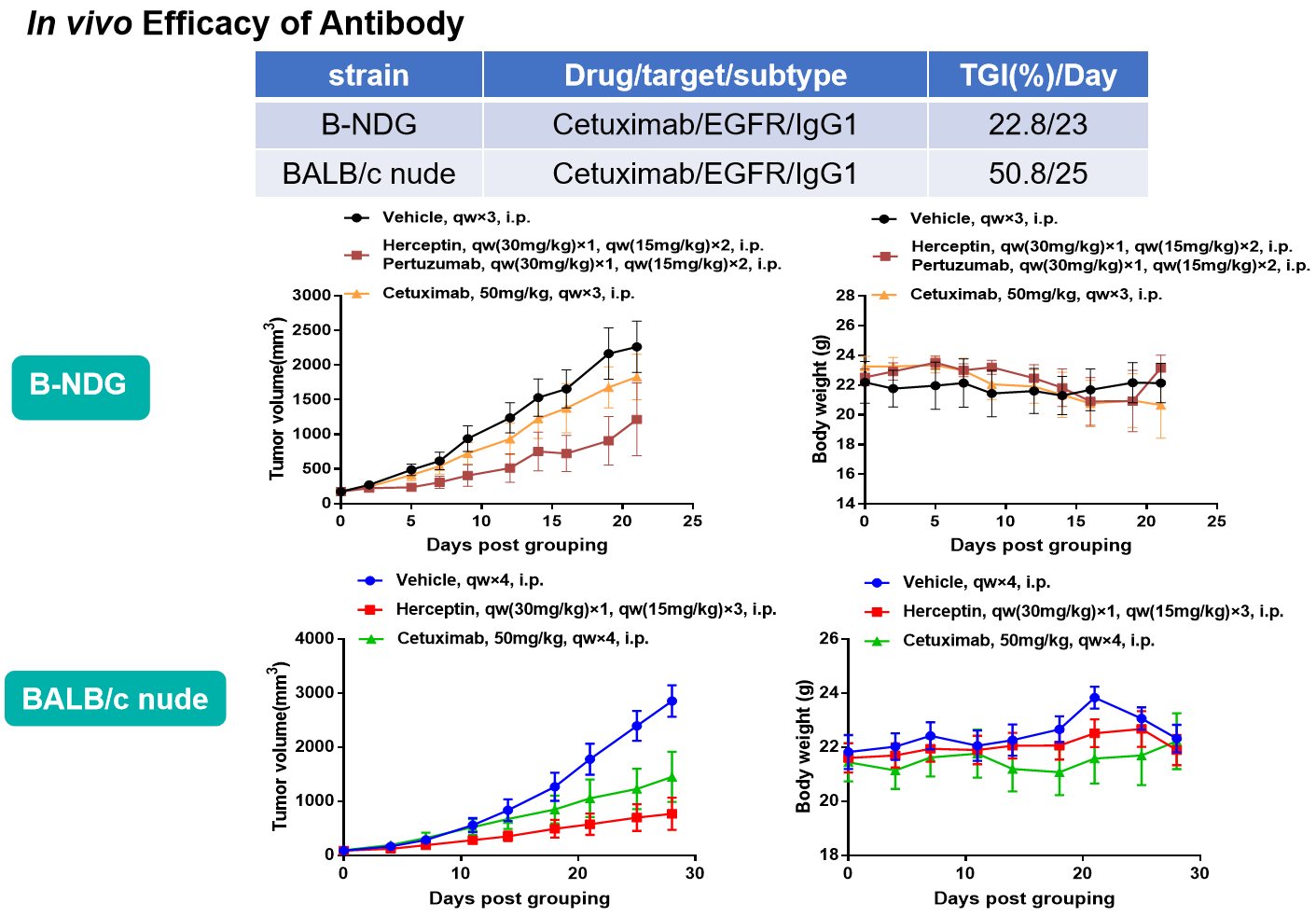
- In vivo Efficacy of Antibody






 +86-10-56967680
+86-10-56967680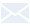 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn