Biocytogen offers comprehensive in vitro cell function evaluation services. Using primary cells and cell lines, we will evaluate the in vitro pharmacology of candidate antibodies, including their binding capacity and Fc- and Fab-related properties, by applying flow cytometry, ELISA, HTRF, Incucyte cell imaging, and other techniques. This will help interpret the efficacy and toxicity mechanisms of candidate antibodies as well as support clinical translational studies.



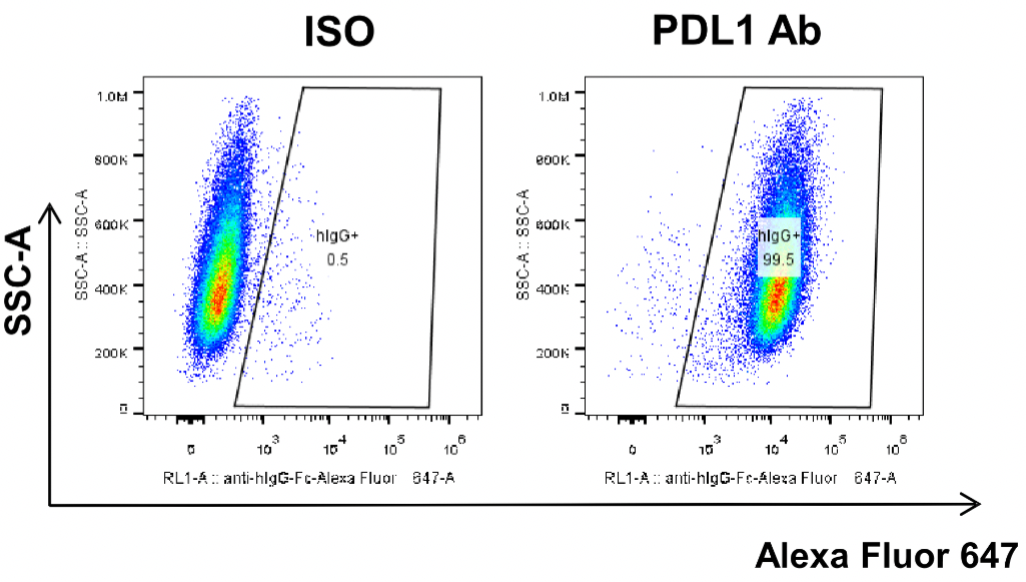
MC38-hPD-L1 was obtained by modification of MC38 cells to replace mouse PD-L1 gene with human PD-L1 gene. Human PDL1 antibody was added first to co-incubate with MC38-hPD-L1 cells, and then fluorescence-labeled secondary antibody was added. Specific binding of the test antibody to the cells was detected by flow cytometry.
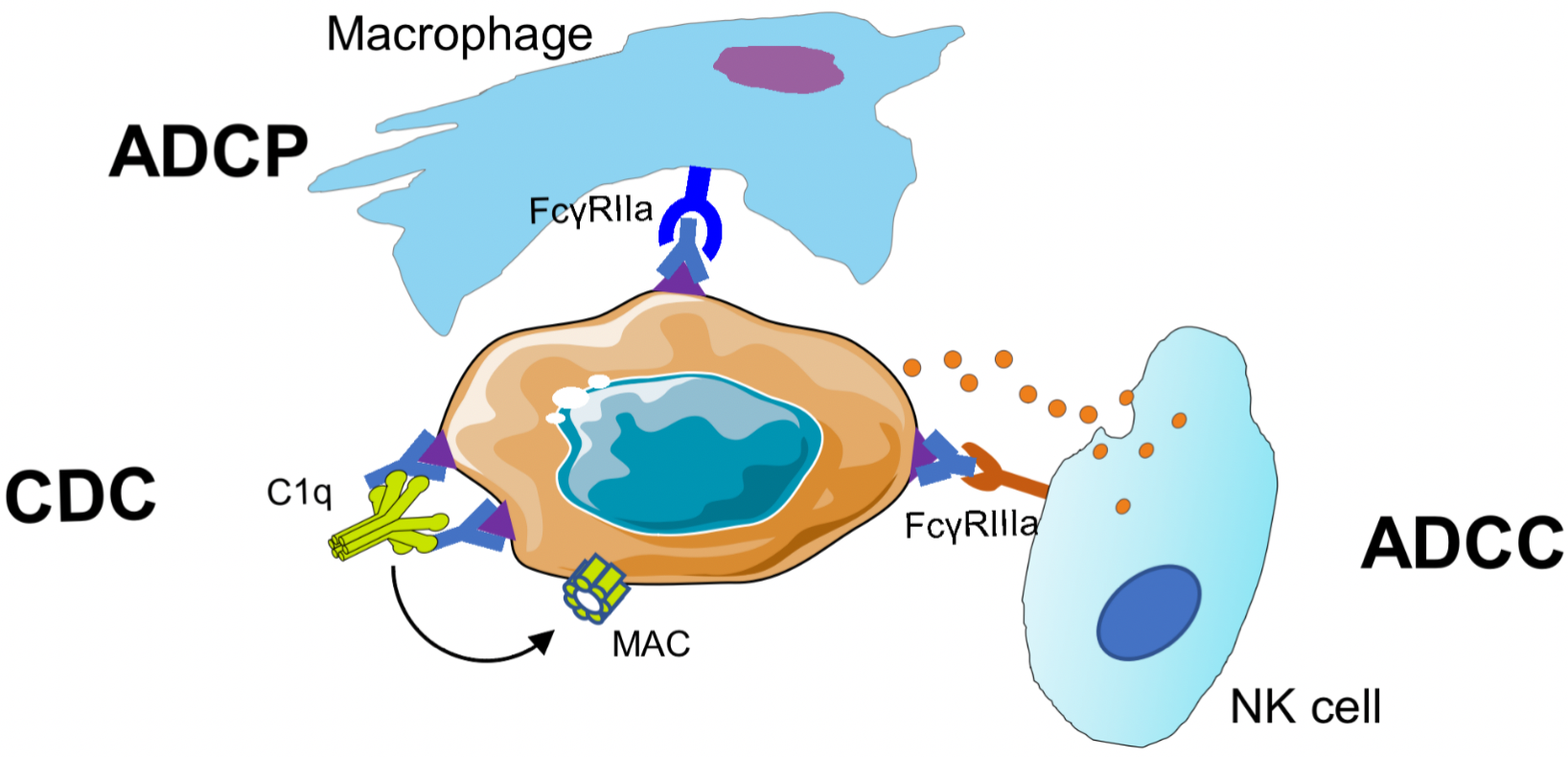
ADCC
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC): Antibody Fc binds to Fcγ RIIIa located on the surface of human NK cells, macrophages, or monocytes, inducing effector cells to secrete perforins and granzymes to kill target cells.
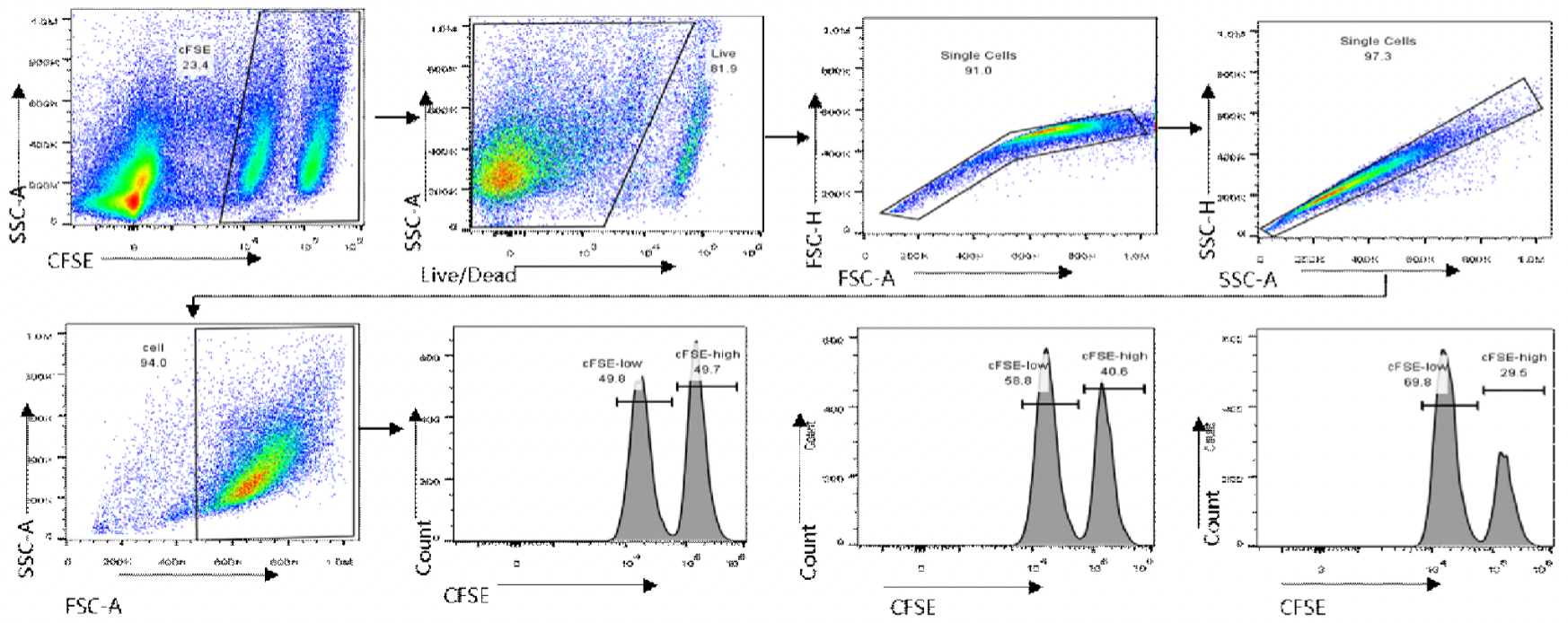
ADCC-FACS Aassay

In this experiment, human PBMCs were used as effector cells. Jurkat-hCTLA4 cells labeled with high-concentration of CFSE were used as target cells, and Jurkat WT cells labeled with low-concentration CFSE as control cells. The effector cells, target cells, and control cells were incubated for 18 h in the presence of different concentrations of anti-human CTLA-4 antibody.
Specific cytotoxicity = [1 − (control well ratio/test well ratio)] 100%;
Ratio = (CFSElow cell count/CFSEhigh cell count)
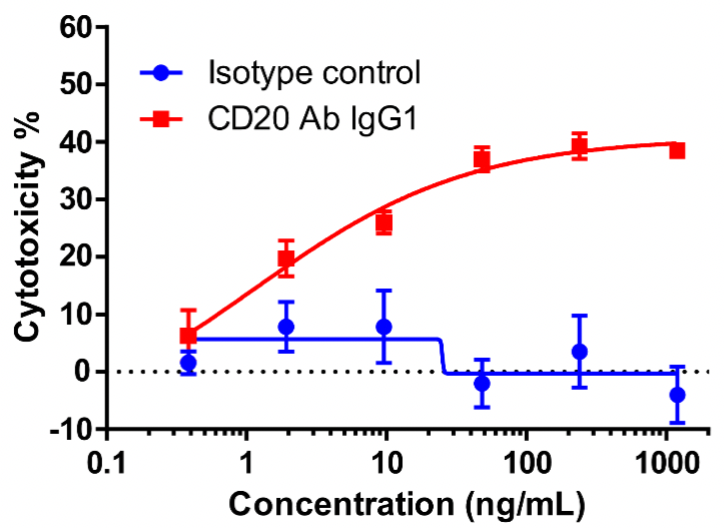
ADCC-LDH Assay
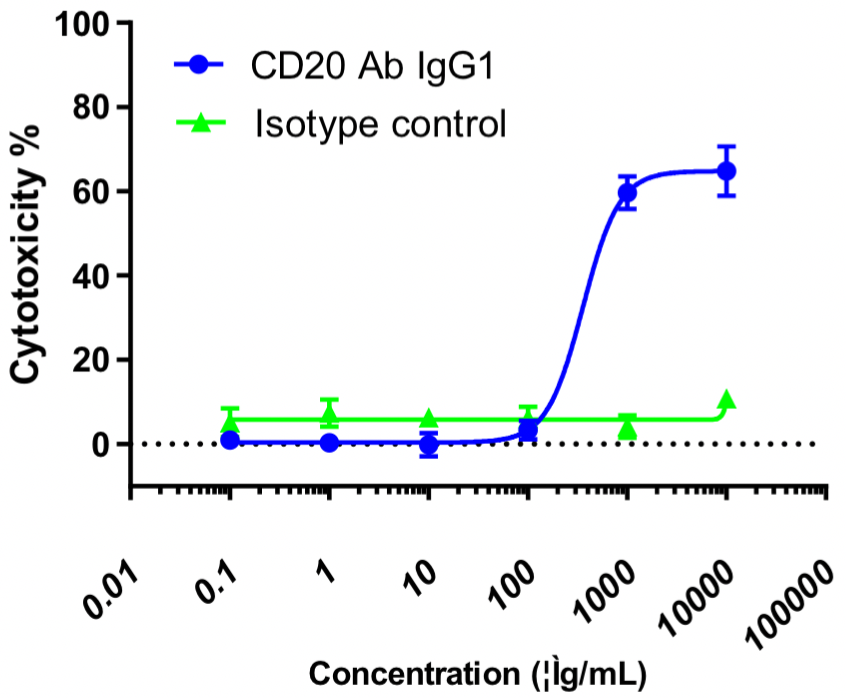
In this experiment, human PBMCs were used as effector cells (E), and Raji cells as target cells (T); E:T = 10:1. Different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies were added and the killing effect was detected by the LDH method after overnight incubation.
ADCC-Incucyte Assay
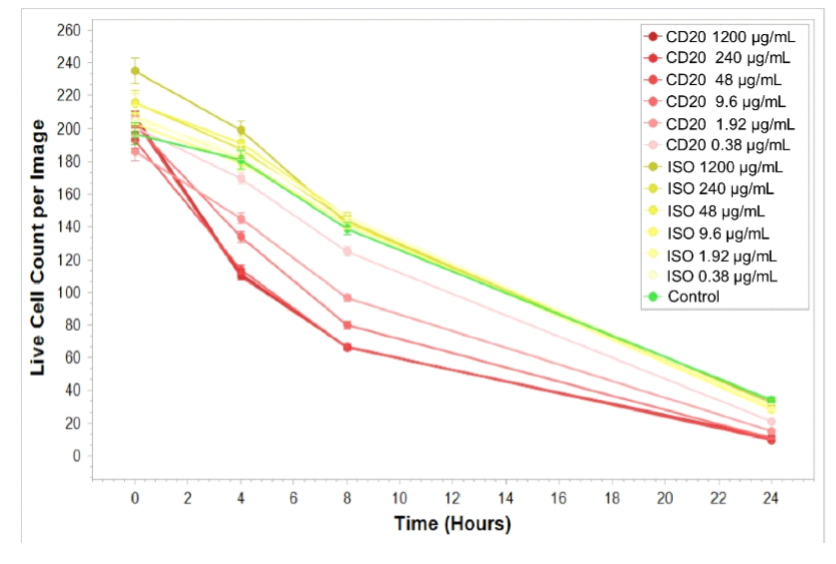
NK cells were used as effector cells (E) and CFSE-labeled Raji cells as target cells (T); E:T = 5:1. Different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies were added, and low concentrations of PIs were added to the culture medium, which was placed at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and photographed every 4 h by Incucyte. At the time point of 4 h, the number of viable CFSE+ cells per well was analyzed to compare the ADCC effects of CD20 antibodies at different concentrations.
Cytotoxicity % = 1 − (number of viable cells in test wells)/(number of viable cells in control group) × 100%
ADCP
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP): Antibody Fc binds to Fcγ RIIa located on the surface of human macrophages/monocytes, inducing the phagocytosis of target cells by macrophages.
ADCP-FACS Assay
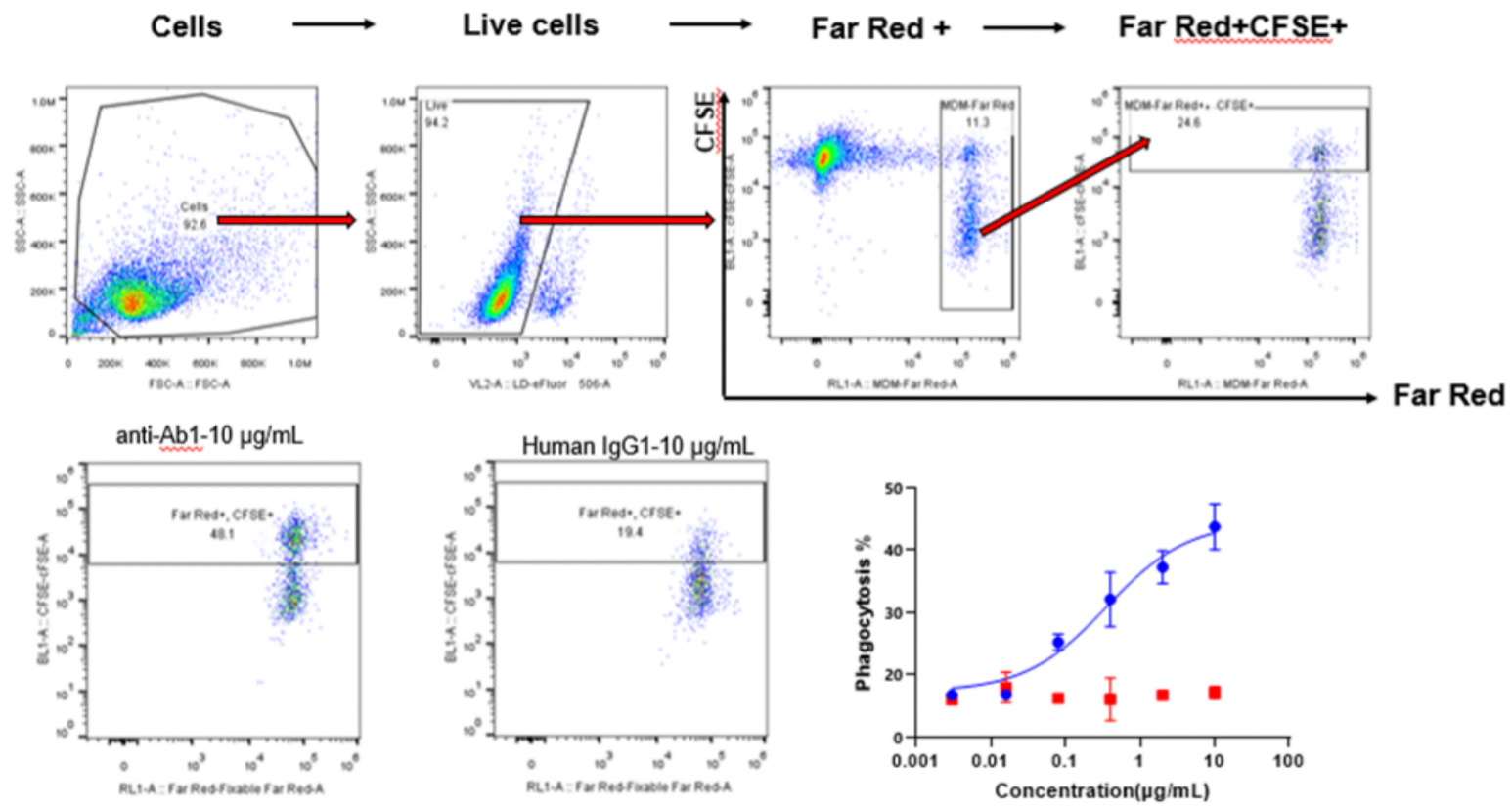
Far Red dyes were used to label macrophages (E), and CFSE dyes were used to label Raji cells (T). E:T = 1:5. Different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies were added and incubated for 4 h, and the phagocytosis of macrophages was detected by flow cytometry.
Phagocytic Index (PI) = (number of ingested macrophages)/(total number of macrophages) × 100%
CDC
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC): The binding of antibody Fab to target cells exposes the complement binding site in the hinge region of the antibody, which is followed by binding to complement C1q. Then C2-C9 is activated to form a Membrane Attack Complex (MAC), which perforates the surface of target cells and exerts a lytic effect on them.
CDC-LDH Assay
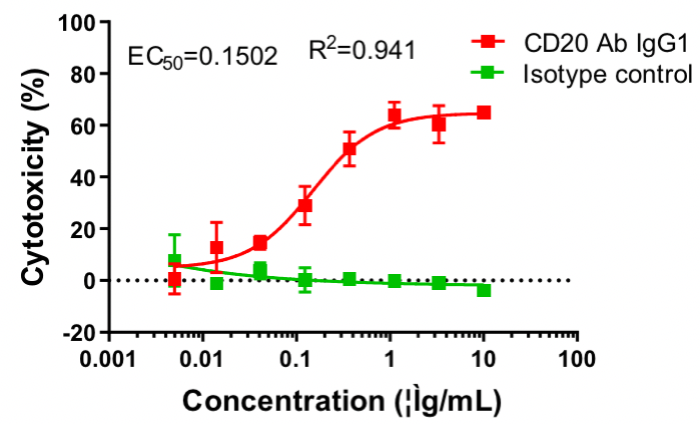
CD20 IgG1 antibody-mediated CDC assay. Raji cells were mixed with different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies in the presence of complement and then incubated for 2 h. The cytotoxic effect of antibodies was detected by the LDH method.
Cytotoxicity % = (LDH value of test wells − LDH value of spontaneous release wells)/(maximum LDH release from target cells − LDH value of spontaneous release wells) × 100%
CDC-Incucyte Assay
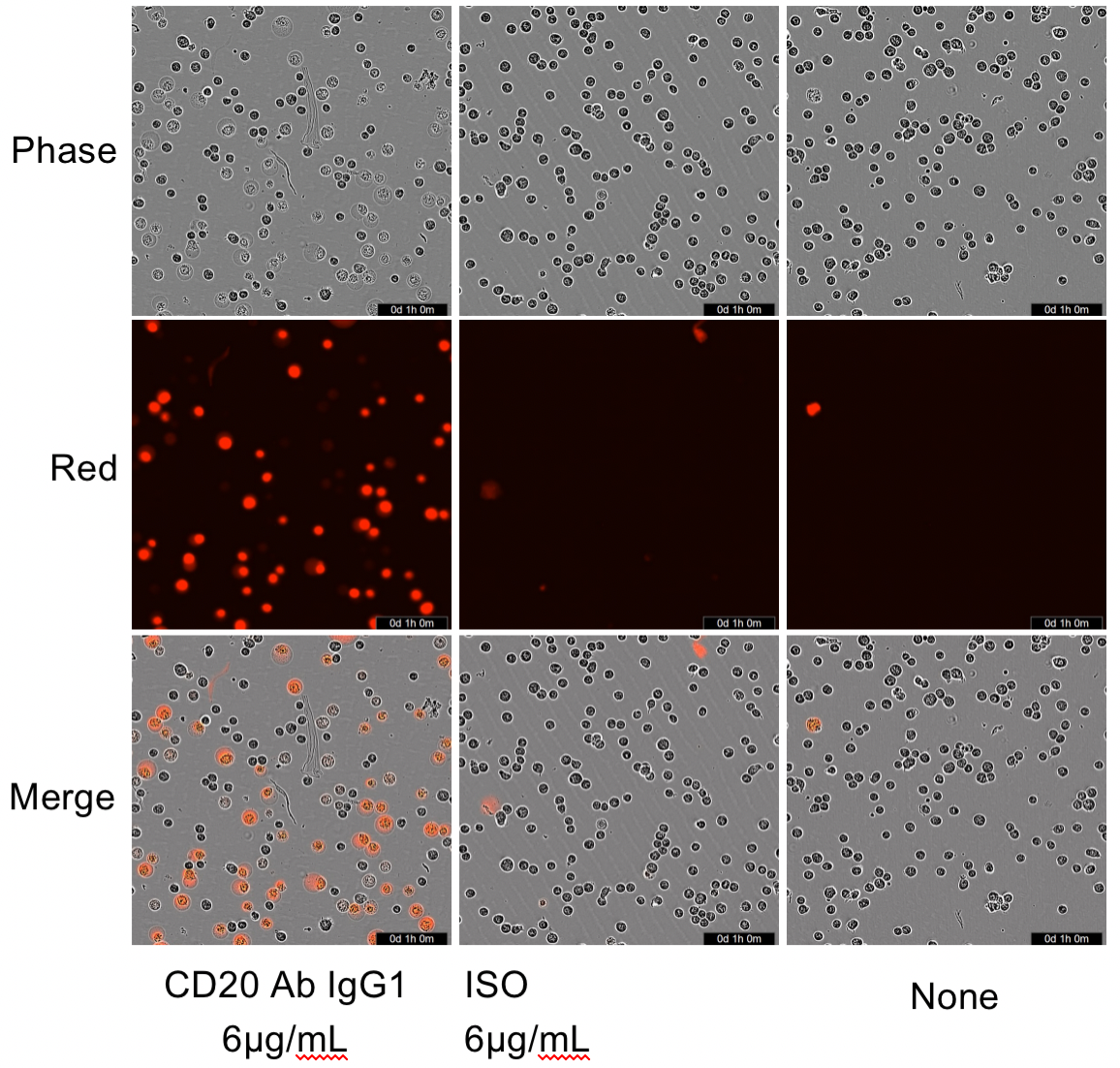
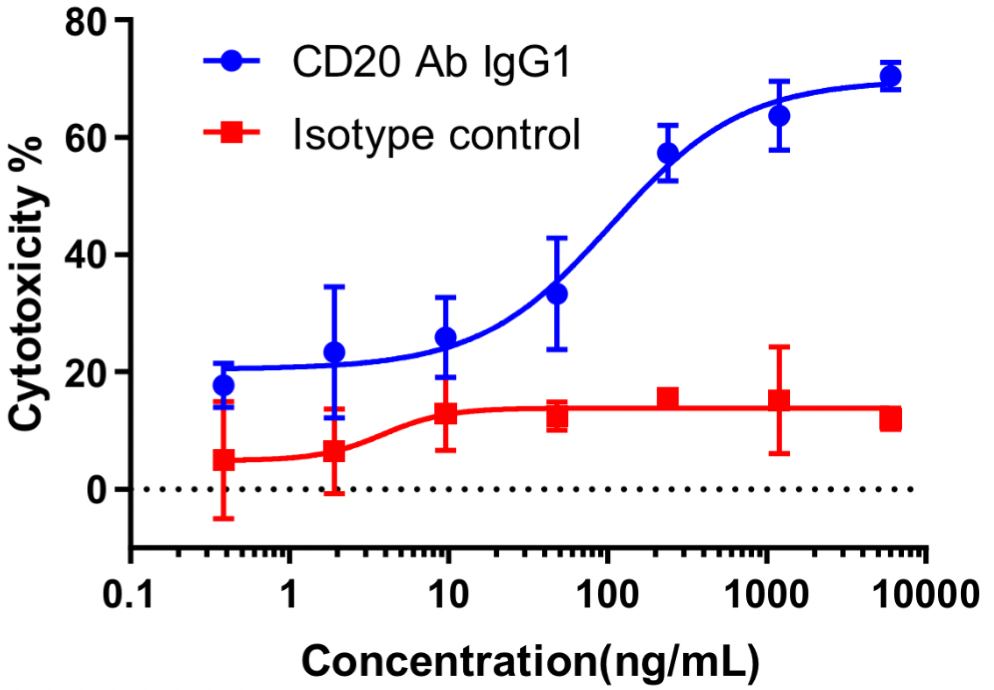
Raji cells were mixed with different concentrations of CD20 IgG1 antibodies in the presence of complement, and low concentrations of PIs were added to the culture medium, which was then placed at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and photographed at 2 h by Incyte.
Cytotoxicity % = 1 − (number of viable cells in test wells)/(number of viable cells in control group) × 100%
a.Effector Cell Activation
Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction (MLR)
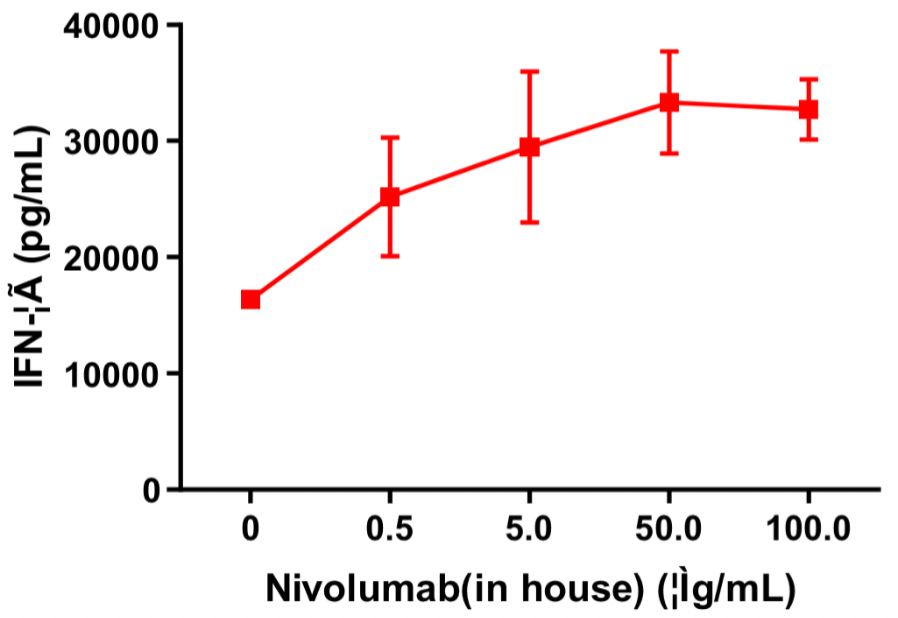
Human CD4+ T cells and allogeneic dendritic cells were mixed in a 96-well round-bottom plate at a ratio of 10:1, different concentrations of nivolumab (in house) were added, and the content of released IFN-γ was measured by ELISA after 120 h of incubation. The results showed that nivolumab (in house) dose-dependently enhanced IFN-γ production in the mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR).
T-Cell Activation Assay
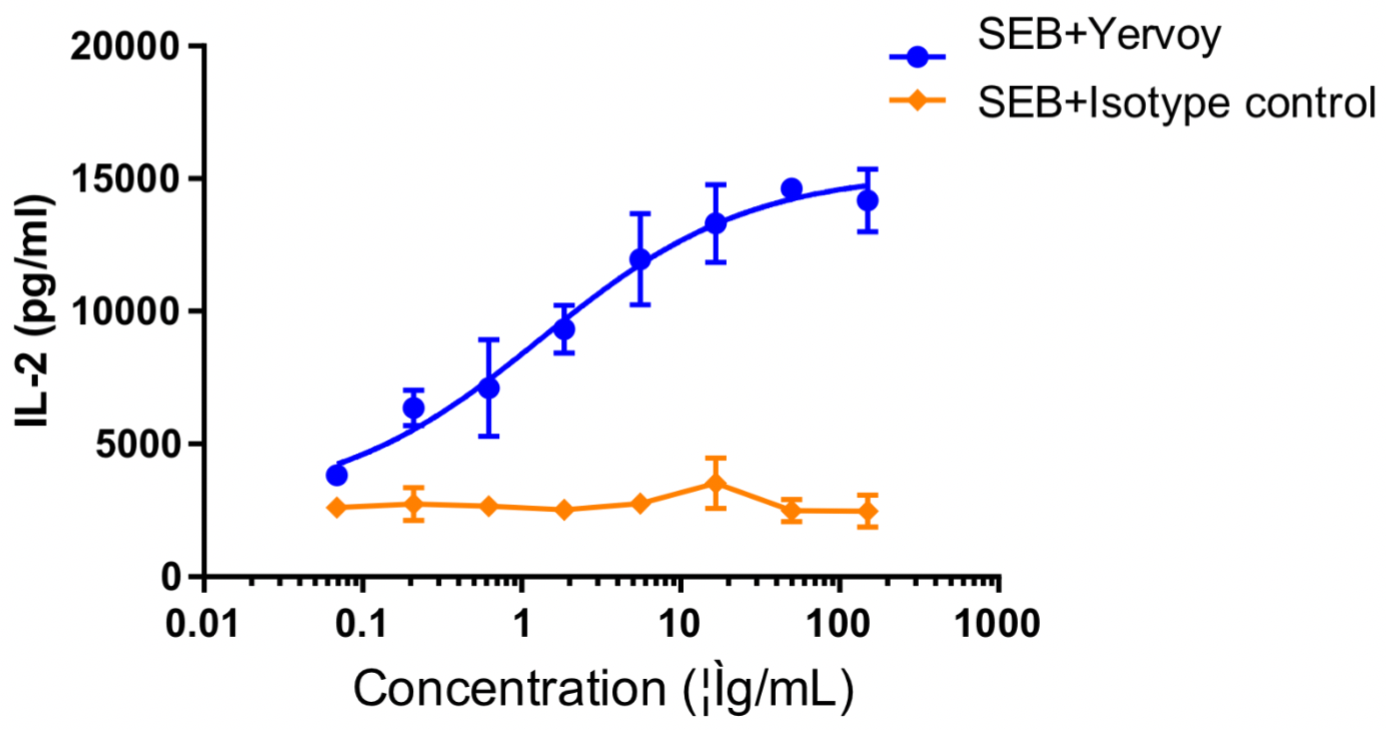
Human PBMCs were co-incubated with SEB (10 ng/mL), followed by the addition of different concentrations of ipilimumab or isotype control antibodies and then further incubation for 48 h. The release of IL-2 was measured by ELISA. The results showed that ipilimumab dose-dependently enhanced IL-2 production by SEB-stimulated PBMC.
b. Enzyme Activity Blockage
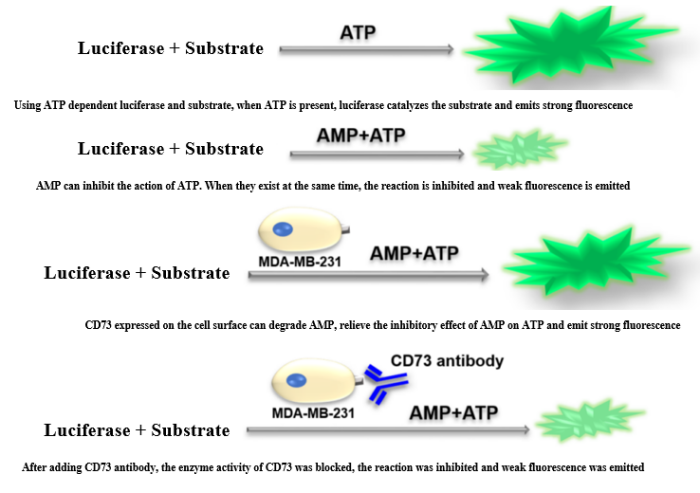
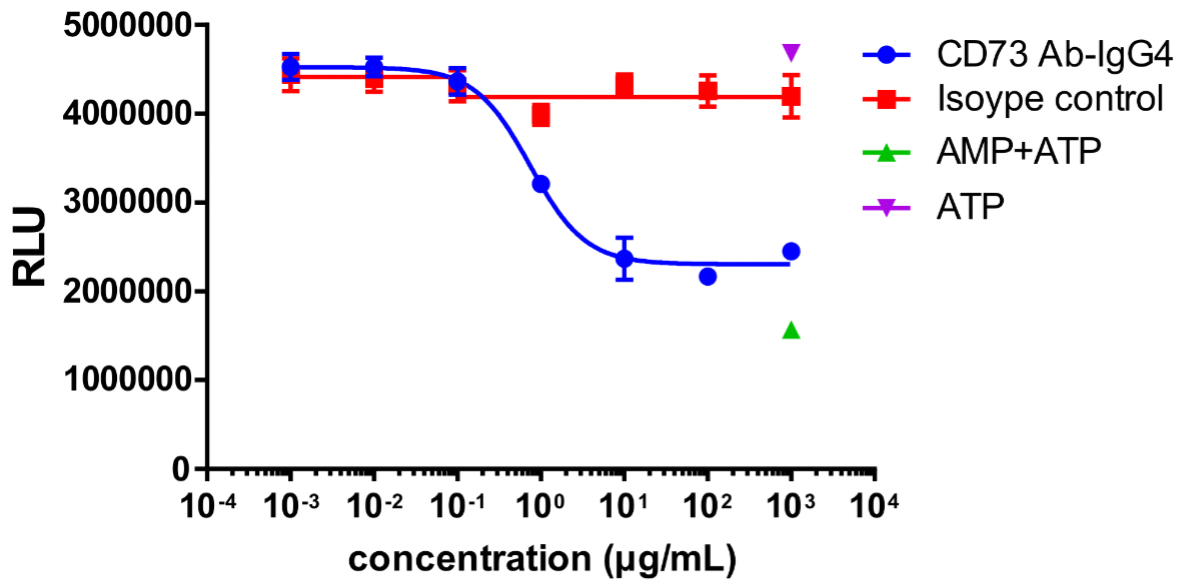
MDA-MB-231 cells were used as target cells and incubated with different concentrations of CD73 antibodies at 37 °C for 30 min; AMP was added and incubated for 3 h; ATP and luciferase + substrate were then added to detect the fluorescence value.
CD73 enzyme activity was inhibited, and the fluorescence value decreased with the increasing concentration of CD73 antibody.
c.Target Cell Proliferation Inhibition
Cell Proliferation-CTG Assay
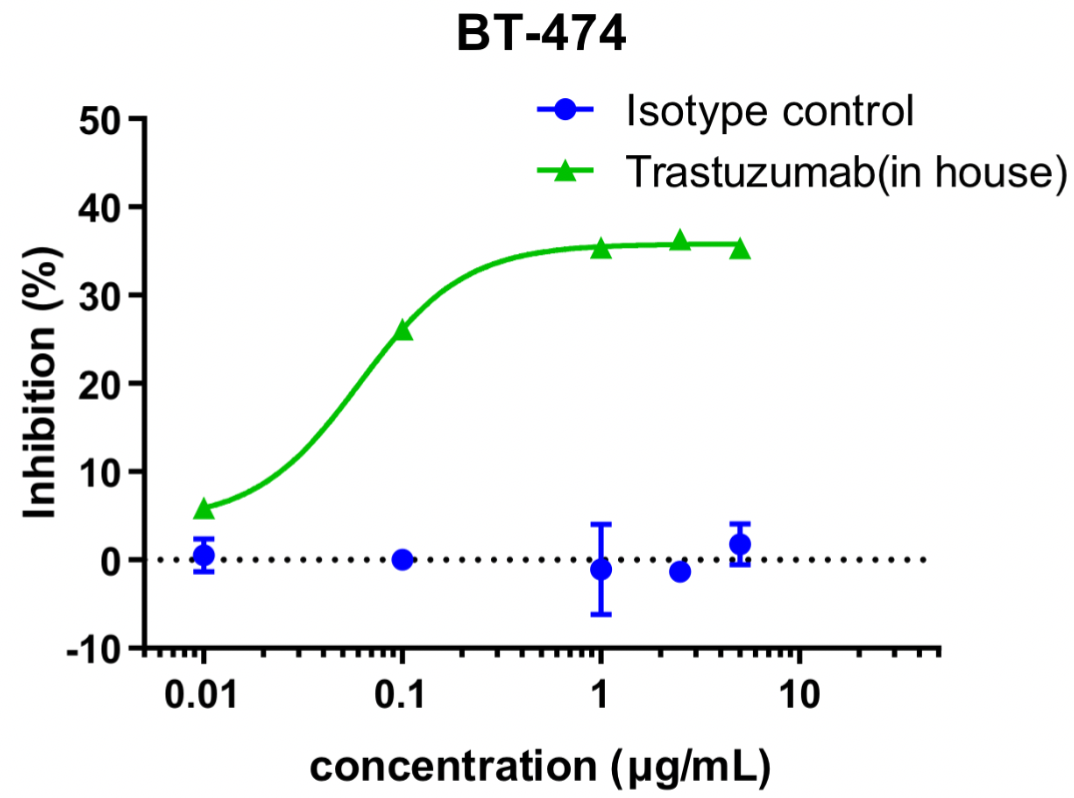
Different concentrations of trastuzumab (in house) were added to BT474 cells for co-incubation, and cell proliferation was detected by the CTG method after 72 h. The results showed that trastuzumab (in house) dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of BT474 cells.
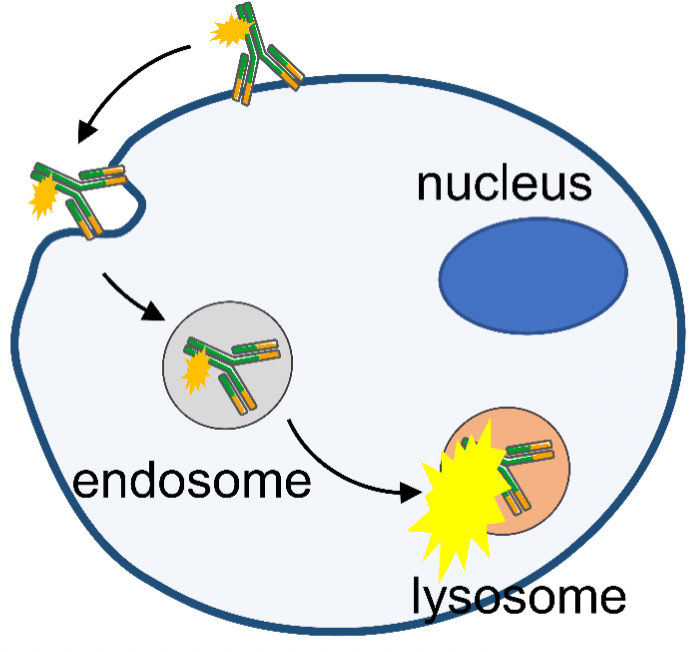
d. Antibody Endocytosis Assay
Antibodies were labeled with pH-sensitive dyes and entered lysosomes after endocytosis. In the lower pH of the lysosome, the dyes emitted a strong fluorescence. Endocytosis of antibodies by cells was detected using flow cytometry.
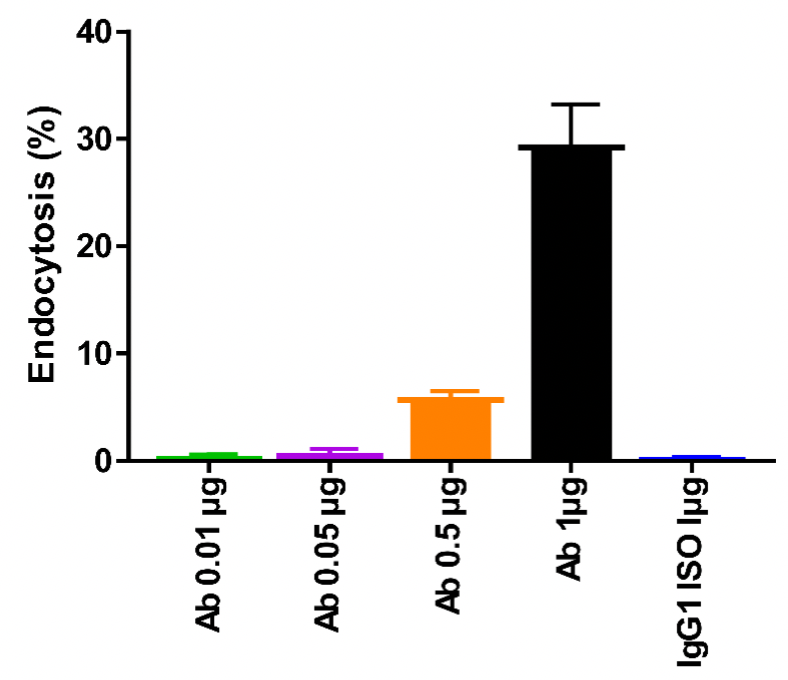
CLDN18.2 antibodies labeled with pH-sensitive dyes were added to MC38-hCLDN18.2 cells and the endocytosis of antibody was detected by flow cytometry after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2. Endocytosis was enhanced gradually with the increasing antibody concentration.






 +86-10-56967680
+86-10-56967680 info@bbctg.com.cn
info@bbctg.com.cn